What is Cosmos (ATOM)?

One of the main stumbling blocks of most cryptocurrencies today is interoperability or inter-blockchain communication capability. For users, Interoperability is the ease of moving their assets across multiple blockchain networks. Currently, moving crypto requires fairly expensive transaction fees and several complicated steps. However, several crypto blockchain networks have started to think about interoperability built into the core of their networks and one of them is Cosmos. So, what are ATOM and the cosmos network? How does it solve the blockchain interoperability problem? This article will cover Cosmos in detail.
Article Summary
- 💻 Cosmos is a technology that allows various blockchains to connect and share data with each other within a shared ecosystem.
- 🌐 All blockchain within the Cosmos ecosystem can communicate with each other using the IBC protocol. This communication can occur due to the use of the same software kit throughout the network, namely the Cosmos SDK and the Tendermint consensus algorithm.
- ️ ⚙️ The Cosmos network will undergo a major update in 2022. Deployment of the Theta upgrade will bring liquid staking, interchain security, interchain accounts, and a blueprint for bringing NFTs to the Cosmos ecosystem.
Definition of Cosmos (ATOM)
Cosmos is a decentralized network connecting a set of blockchains that work independently within a single ecosystem. This has earned Cosmos the nickname ‘internet of blockchains’. As the name suggests, imagine Cosmos as a huge galaxy containing hundreds of blockchains as its planets.
Cosmos can do this by issuing a software development kit (SDK) for developers who want to create a blockchain on the Cosmos network. The SDK makes it easy for many developers because they don’t have to build their own blockchain from scratch so they can focus on things like decentralized application creation (DApps). Furthermore, the SDK also ensures compatibility within a shared ecosystem.
The Cosmos network native cryptocurrency is ATOM, which acts as a staking and governance token. According to Coinmarketcap, Cosmos is the 19th largest crypto asset in the world with a market capitalization of $9.3 billion dollars. ATOM itself has a maximum supply of 286,370,297 at a price of $32.5 dollars per 1 ATOM (January 24, 2022).
History of Cosmos
The birth of the Cosmos network began with Tendermint, a proof-of-stake (PoS) consensus algorithm created by Jae Kwon, Zarko Milosevic, and Ethan Buchman in 2014. Consequently, The formation of the Cosmos network was coordinated by two non-profit organizations, Tendermint, inc. and The Interchain Foundation (ICF). Cosmos conducted an ICO in 2017 and raised $17 million dollars. Then, the Cosmos mainnet was successfully launched in March 2019 and Jae Kwon stepped down as CEO in February 2020.
The development of the technical side of the Cosmos network is led by Tendermint, Inc. chaired by Peng Zhong. Currently, the Cosmos network has 262 applications consisting of various decentralized applications, blockchain, and other services.
Also read: Whitepaper Cosmos
How Cosmos works

Basically, Cosmos is a decentralized network running multiple independent blockchain networks that work in parallel. The Cosmos network and all its blockchain use a PoS consensus algorithm called Tendermint Core. Tendermint is a consensus algorithm that utilizes BFT technology which allows transactions confirmation to occur even if some of the validators act maliciously or strangely.
Also read: What is a proof-of-stake (PoS) consensus algorithm and how does it work?
💡 What are ‘layers’ in cryptocurrency?
Layer 0: The network that acts as the foundation that supports the creation of a blockchain network on top of it and creates interoperability for the ecosystem. Example: Polkadot, Cosmos.
Layer 1: The main blockchain infrastructure with a capacity to build an ecosystem of applications and services. Example: Ethereum, Bitcoin, Terra, and Solana.
Layer 2: A network specifically built to improve the performance and capabilities of Layer 1 below it. A layer 2 can only be built on top of another blockchain network. Example: Polygon Matic.
Cosmos is often referred to as blockchain layer 0 because it becomes a platform for other blockchains to operate. Through the Cosmos network, its blockchains can communicate with each other and facilitate the movement of cryptocurrencies and transactions across multiple chains. Cosmos wants to be a solution to the blockchain interoperability problem.
Hubs and zones
Cosmos uses the concepts of hubs and zones to distinguish between Cosmos’ central network and the blockchains around it. Hubs and zones interact like a transportation system such as airport or train station. Cosmos acts as a hub connecting the small zones within it in a decentralized manner. Like an airport, Cosmos is a central airport that facilitates and handles transit from one country to another.
In a blog created by the ICF, Cosmos refers to itself as a virtual port city. This interaction between hubs and zones is possible because all applications and blockchain within the Cosmos ecosystem use the same set of programming tools which are Cosmos SDK and the Tendermint consensus algorithm.
💡 What is Cosmos SDK?
The Cosmos SDK is a set of programming tools containing modules for building applications that conform to the standards of the Cosmos ecosystem. This module creates interoperability for all blockchain and applications built on the Cosmos network.
Several blockchains utilizing the Cosmos SDK
- Terra
- Thorchain
- Binance Chain
- Crypto.com (CRO)
- Oasis Network (ROSE)
- Kadena (KDA)
Cosmos IBC

Then, how does Cosmos allow communication between blockchain networks to occur? How can each zone communicate with the others? The answer is the Cosmos IBC protocol or Inter-Blockchain Communication. Cosmos launched the IBC protocol in March 2021. Simply put, IBC is a protocol that allows blockchains to talk to each other. If Cosmos acts like an airport, the IBC protocol is the plane that makes this movement possible.
However, application developers must meet several technical requirements in order to take advantage of the IBC protocol. A blockchain that cannot meet IBC requirements such as Bitcoin or Ethereum can take advantage of Gravity Bridge technology. Thus, The blockchain bridge can facilitate the movement of cryptocurrencies from external networks (such as Ethereum) into the Cosmos ecosystem and vice versa. On January 19, 2022, Gravity Bridge Cosmos-Ethereum was successfully launched.
Currently, the functionality of the IBC protocol is still very limited and developers within the Cosmos network do not yet have a major incentive to use IBC. However, many Cosmos updates will add functionality to the IBC protocol such as interchain security, interchain accounts, and NFT integration. Some of these updates have the potential to be a catalyst and impetus for developers on the Cosmos ecosystem to take advantage of the IBC protocol. More widespread adoption of IBC can improve Cosmos network interoperability and use of the ATOM token.
What can you do with ATOM?
Staking
Like a blockchain network with a PoS algorithm, Cosmos allows you to stake using ATOM. According to stakingrewards, the average interest you get from staking Atom is around 11-14%. If you do it through Cosmos Hub, you will earn 9.7%. Staking is one of the easiest ways to get passive income from your crypto assets. You need to be careful in depositing your money when staking because you can lose your assets if the validator you choose cannot be trusted.
Using the DApps on the Cosmos ecosystem
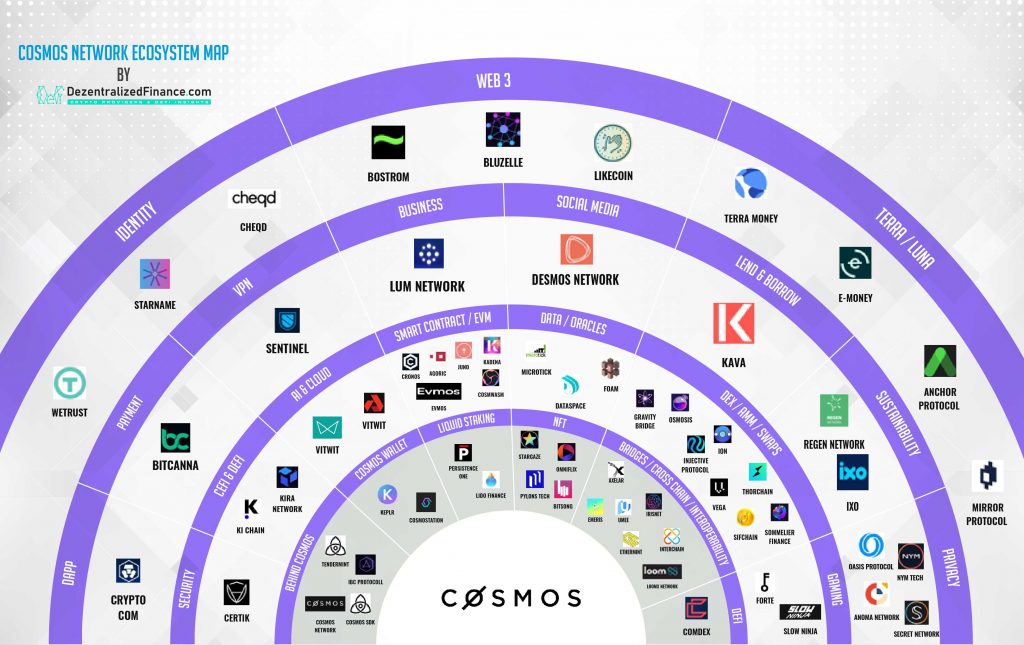
The Cosmos ecosystem includes an extensive network containing various types of crypto services ranging from blockchain such as Terra, centralized exchanges such as Crypto.com, to decentralized financial applications like Anchor Protocol. Currently, if you want to use the Anchor Protocol using ATOM, you still have to convert ATOM tokens into UST manually. However, this will change with the interchain account feature which allows you to have a single crypto wallet that can be used in several different blockchains within the Cosmos ecosystem.
- Gravity DEX: Gravity DEX is a decentralized cryptocurrency exchange for tokens on the Cosmos network. Moreover, Gravity also wants to build a bridge to facilitate the movement of assets from outside the Cosmos network with low transaction fees.
- Osmosis: Osmosis is a Uniswap-based automatic market makers (AMM) application that allows you to create a liquidity pool (LP) for all tokens that exist in the Cosmos ecosystem. You can deposit assets in one of these LPs and earn up to 100% interest.
- ️ Emeris: Emeris is a decentralized cryptocurrency exchange (DEX) dedicated exclusively to Cosmos ecosystem tokens for trading and profiting from LP. Emeris is built on top of Gravity DEX and will benefit from an upcoming IBC protocol update.
ATOM as an investment
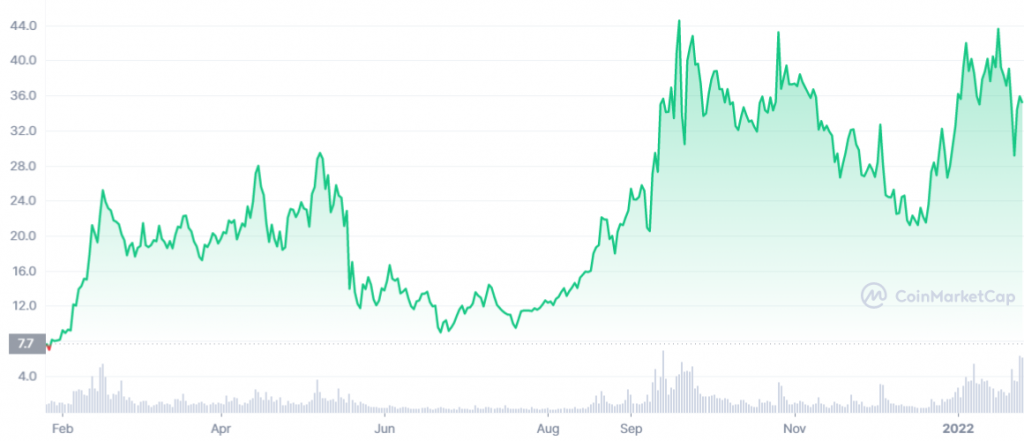
In 2021, ATOM recorded an all-time high in September 2021 at a price of $44.7 dollars. In the past year, ATOM prices recorded a price increase of approximately 332%. This increase is considered quite small compared to the price of other altcoins such as LUNA and MATIC whose prices jumped thousands of percent in 2021. Those who buy ATOM in June-August 2021 get a profit of up to 500% when ATOM experiences a pump in September-November 2021. When LUNA, MATIC, and FTM are up more than 1000% in 2021, the ATOM price increase is considered small.
This is due to several internal factors of the Cosmos network. First, in early to mid-2021 ATOM has no use other than as a staking token. In this period, many applications built on the Cosmos network are still in the testing phase. Second, many blockchains in the new Cosmos ecosystem have only taken advantage of IBC features in Q3-Q4 2021 such as Terra. Lastly, Cosmos network updates are mostly targeted for 2022. We could see ATOM starting to show its strength in late 2021 and potentially carrying it over to early 2022.
Concerns regarding ATOM
One of the concerns about ATOM is the questions mark about how quickly it can roll out some crucial updates. The Theta upgrade will bring liquid staking, intechain accounts, intechain security, and a blueprint for the creation of NFTs on Cosmos. Cosmos plans to implement the Theta update in Q1 2022. There are questions whether this target is achievable or whether the upgrade will be as important as it is described. Furthermore, The hype around ATOM is now so big that if the update does not deliver, it will disappoint a lot of holders. As always, Don’t forget to do fundamental and technical analysis before investing in any crypto asset.
ATOM tokens roadmap
Cosmos’ developers made an article outlining the 2022 roadmap, especially some of the milestones they want to achieve in the upcoming year. Most of these milestones will be achieved via an update called Theta planning to launch in Q1 2022.
- 🔒 Interchain Security: The interchain security update allows all blockchain within the Cosmos ecosystem to ‘lend’ security to each other via sharing the network of validators. This is done to support newer blockchains and applications which do not yet have a lot of validators to process transactions. This update will also allow You to get staking rewards from multiple blockchains using only ATOM tokens.
- 👥 Interchain Account: The Interchain account feature gives you the ability to use various DeFi applications within the Cosmos ecosystem without having to exchange your crypto assets using bridge or DEX into another wallet. An interchain account makes it easy for you to use different blockchains and keep all of your IBC compatible assets in one place.
- 💸 Liquid Staking: Theta update will bring liquid staking feature for ATOM token holders. Liquid staking allows you to change your staked ATOM into bATOM or bonded ATOM which you can use in other applications within the Cosmos ecosystem.
- ️ 🖼️ NFT: Cosmos says the Theta upgrade will also be bringing the necessary features to bring NFT to the Cosmos network. The Stargaze Protocol will also be launched at the same time to support the creation of a vibrant NFT community within the ecosystem.
Buying ATOM
You can start investing in Cosmos by buying ATOM in the Pintu app. Through Pintu, you can buy ATOM and other cryptocurrencies in an all-in-one convenient application.
Pintu is also compatible with popular wallets such as Metamask to facilitate your transactions. Download the Pintu app on Play Store and App Store! Your security is guaranteed because Pintu is regulated and supervised by Bappebti and Kominfo.
References:
- What is Cosmos? – Cosmos Network, accessed on 24 January 2022.
- Whitepaper – Resources – Cosmos Network, accessed on 24 January 2022.
- What is Cosmos? (ATOM), Kraken, accessed on 24 January 2022.
- Ki Chong Tran and Daniel Phillips, What Is Cosmos (ATOM)? | The Beginner’s Guide, Decrypt, accessed on 24 January 2022.
- What is Cosmos (ATOM) | History, Roadmap, Economics, Messari, accessed on 25 January 2022.
- Cosmos Network, Inter Blockchain Communication (IBC) And Its Value in The Cosmos Hub, Hacker Noon, accessed on 26 January 2022.
- Understanding Cosmos Network: The Internet of Blockchains, Hacker Noon, accessed on 27 January 2022.
- Billy Rennekamp, Interchain Security is Coming to the Cosmos Hub, Cosmos Blog, accessed on 27 January 2022.
- Christina Cosmos, What’s Coming to Cosmos in 2022?. With another incredible year behind us, Cosmos Blog, accessed on 27 January 2022.
Share
Related Article
See Assets in This Article
BNB Price (24 Hours)
Market Capitalization
-
Global Volume (24 Hours)
-
Circulating Supply
-