Cosmos Ecosystem Upgrade and ATOM 2.0
Bringing the concept of the “Internet of blockchains”, Cosmos has become a big player in the crypto industry since its launch in 2019. Together with Polkadot, it is a “layer-0” technology that forms the foundation for other blockchains that are built on top of it. The technology developed by Cosmos allows blockchains to communicate with each other in a decentralized network. The Cosmos ecosystem has native crypto called ATOM. Currently, ATOM does not have much use, as it cannot capture much value from the Cosmos ecosystem. With the ATOM 2.0 whitepaper, the Cosmos team wants to expand the role of ATOM. So, what is ATOM 2.0? This article will describe the changes brought about by the ATOM 2.0 update.
Article Summary
- 🌐 Cosmos is an integrated blockchain network that wants to create an “Internet of blockchains”. It is an ecosystem that contains various interconnected blockchains.
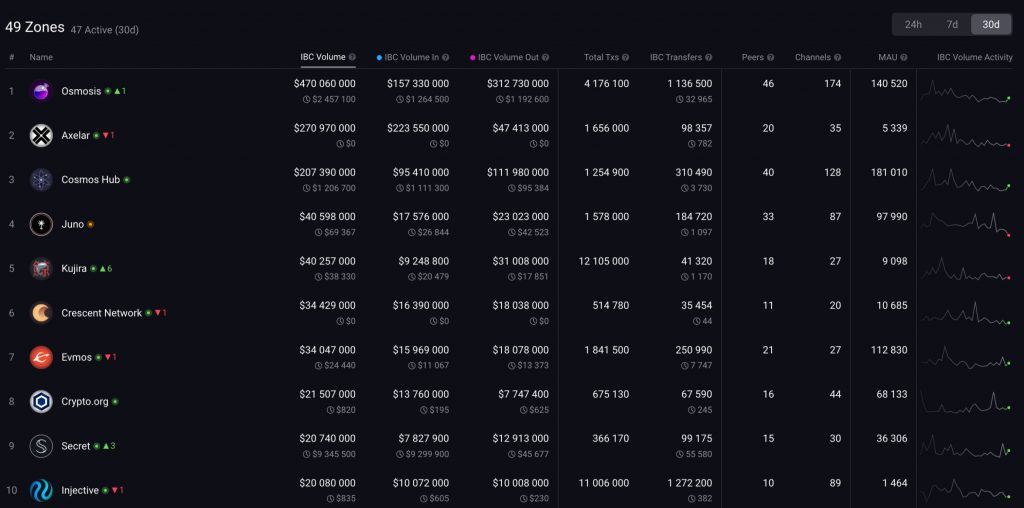
- 🎇 Currently, there are 49 zones within the Cosmos interchain ecosystem. Many of these zones are connected to hubs in charge of forwarding messages between blockchains. Cosmos Hub is a Cosmos-owned hub with ATOM tokens as its native cryptocurrency.
- 🏦 The foundation behind Cosmos explains that the ATOM 2.0 update will transform the Cosmos Hub and ATOM into the economic center of the interchain ecosystem.
- 🔝 This update brings interchain security, liquid staking, interchain scheduler, interchain allocator, and decentralized governance system through Cosmos Councils and Assembly. In addition, the ATOM 2.0 whitepaper proposes changes to ATOM’s tokenomics.
Cosmos Ecosystem and Current ATOM Token
Cosmos is an integrated blockchain network that wants to create an “Internet of blockchains”. The meaning of this jargon is that Cosmos was developed with the aim of connecting various crypto blockchains, like the internet, through programming code that is open to the public.
Cosmos uses several important technology pillars to create an integrated blockchain network. These pillars include Tendermint Core (consensus mechanism), Cosmos SDK (framework for building applications), and IBC Protocol (inter-blockchain communication protocol). These technologies help align all applications and blockchains on top of the Cosmos ecosystem.
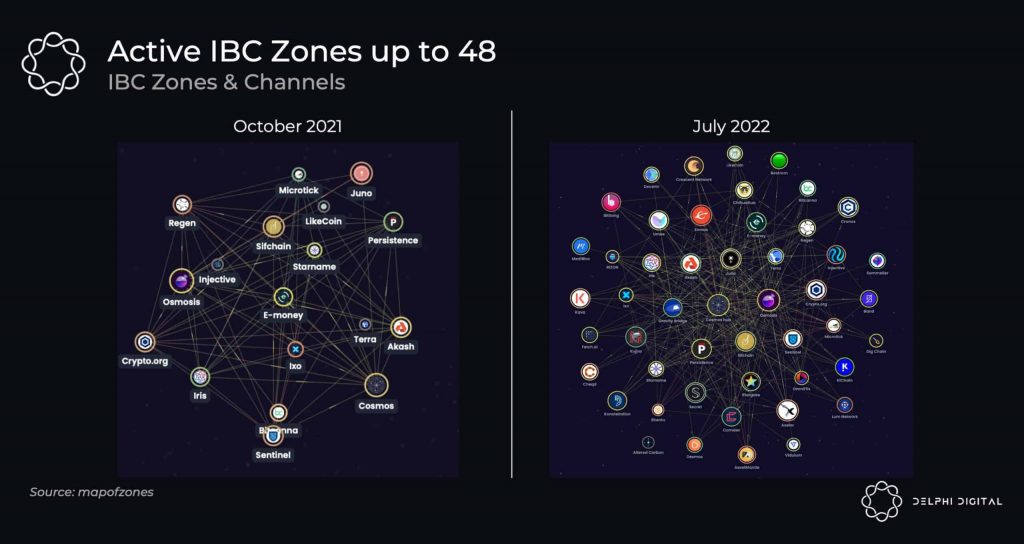
As of October 2022, 49 zones/blockchains (also known as appchains) have been integrated into the Cosmos ecosystem. This number has doubled from the number of zones in October 2021. This rapid development is proof that blockchain developers are very interested in the concept of the Cosmos ecosystem.
💡 Appchains stands for application blockchains. Appchains is a term for protocols that have their own blockchain. Some examples of appchains in the Cosmos ecosystem are Osmosis and Kujira.
Cosmos Hub is a hub created by the cosmos that connects another 40 zones. ATOM is Cosmos native cryptocurrency for paying transaction fees, staking, and votes in the governance system. The role of ATOM is similar to that of ETH on Ethereum. So, Cosmos Hub has a major role in securing the Cosmos ecosystem (via ATOM staking) and running the IBC (Inter-Blockchain Communication) protocol.
Many have explained that Cosmos’ ATOM token has an identity crisis. Many appchains like Osmosis have their own assets and validators so they don’t need ATOM. This leaves ATOM without a value capture scheme and very limited utility. So, although the development of the Cosmos ecosystem is so rapid, it has no effect on the price and the usability of ATOM. Even though ATOM is at the center of the blockchain ecosystem, its value and utility are limited.
Therefore, development stage 2 of the Cosmos ecosystem wants to change this. The Interchain Foundation (the foundation behind Cosmos) wants to overhaul ATOM tokenomics through ATOM 2.0.
What is Atom 2.0?
According to Ethan Buchman, one of the founders of Cosmos, the Cosmos ecosystem has entered stage 2 development called integration. In this phase, the Cosmos development team focused on reconstructing and reintegrating the Cosmos Hub into the centerpiece of the interchain ecosystem. Ethan explains that the Cosmos team wants to create a new economic system that emphasizes utilizing the security provided by the Cosmos Hub. So, the integration phase wants to integrate and harmonize the role of Cosmos Hub and ATOM toward the development of the interchain ecosystem as a whole.
💡 Phase 1 of Cosmos’ development is initiation and focuses on attracting as many crypto projects as possible into the Cosmos ecosystem.
At the Cosmosverse event in Medellín, Colombia, the ATOM 2.0 Whitepaper and the Cosmos Hub ecosystem update are available to the public. The ATOM 2.0 whitepaper describes various updates to the Cosmos ecosystem such as the interchain security, liquid staking, the new ATOM tokenomics, and the new Cosmos governance. The Cosmos development team explained that this whitepaper is still in draft and is subject to change.
Briefly, the new Cosmos proposal has 5 main components:
- Interchain Security
- Liquid Staking
- Interchain Scheduler & Allocator
- New Tokenomics For ATOM
- Cosmos Ecosystem Governance Through Cosmos Assembly & Councils
You can read the new Cosmos whitepaper in this Cosmos Hub forum.
The Interchain Ecosystem Upgrade
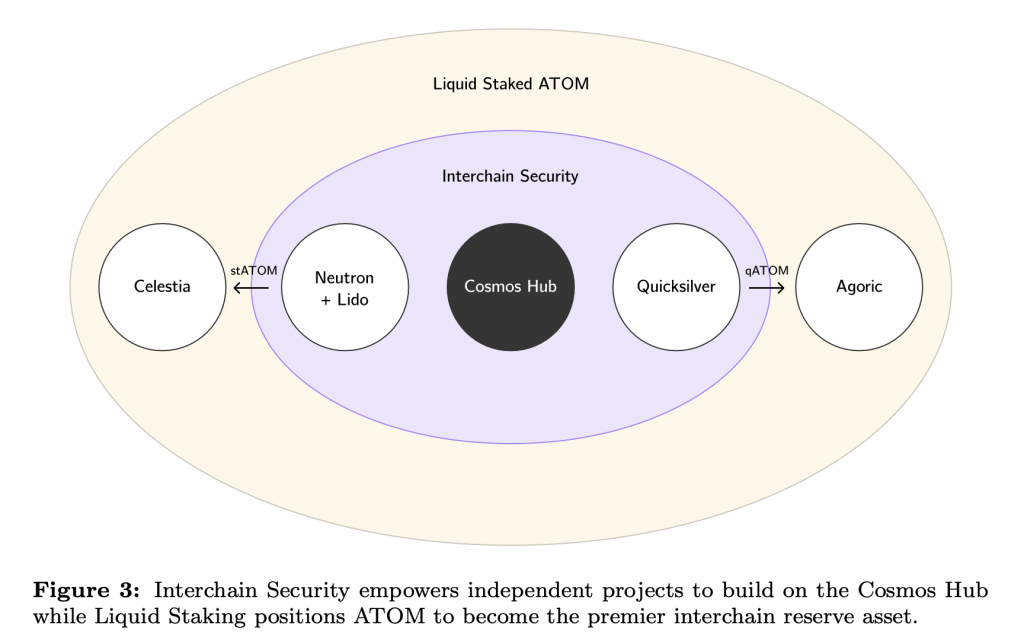
Interchain Security
Interchain Security is an update of Cosmos that will be an important feature of the Cosmos ecosystem. Through Interchain Security, all appchains connected to Cosmos Hub can “borrow” security from Cosmos. They can do that by borrowing from 175 validators Cosmos Hub and paying a certain fee (of which 25% goes to ATOM stakers). Initially, the Cosmos Hub will subsidize some of the fees.
💡 The Cosmos development team also refers to its ecosystem as the interchain ecosystem
This provides an opportunity for the new blockchain to borrow the security from Cosmos rather than having to form its own network of validators. With this, developers can focus on building a user community and just allocating security costs. It also integrates ATOM staking into further zone developments in the Cosmos ecosystem.
The Interchain Security feature can bring crypto projects into the Cosmos ecosystem that don’t have the resources to own a network of validators. It also helps in the process of decentralizing appchains in the Cosmos ecosystem whilst increasing their security.
Liquid Staking
Liquid Staking is a form of staking where locked tokens can still be used in their liquid stake form. This feature is very similar to what Ethereum is using now where users who lock on liquid staking will get sETH equivalent to the token they locked. The difference is, liquid staking on Cosmos will be integrated into the network and not made by a third party like Lido.
The liquid staking feature provides new uses for locked ATOM tokens. With liquid staking, a locked ATOM not only serves to secure the network. ATOM on liquid staking will feed back in various appchains in the interchain ecosystem, forming a positive feedback loop. This will create a new economic cycle in the Cosmos.
New ATOM Tokenomics
The current ATOM issuance system is defined by the balance between liquidity and staking. When ATOM is low on staking, the percentage of staking interest will increase, causing new ATOM printing to go up. On the other hand, the issuance rate of new ATOMs will decrease when the number of ATOMs in staking is high.
💡 In a proof-of-stake network, new ATOM is given to validators who help secures the network and process transactions through staking.
With the advent of liquid staking, the ATOM issuance rate will change. Liquid staking is expected to solve the problem of maintaining a balance between liquidity and staking by attracting many users to use the feature.
Furthermore, the ATOM 2.0 Whitepaper describes two phases in ATOM tokenomics, transition and steady state. In the first phase, the printing rate of the new ATOM will increase in the first 9 months as an incentive and subsidy for appchains who want to use interchain security. In addition, the purpose of increasing the issuance of new ATOM is also aimed at increasing the amount of Cosmos which will later be managed by the Cosmos ecosystem community.
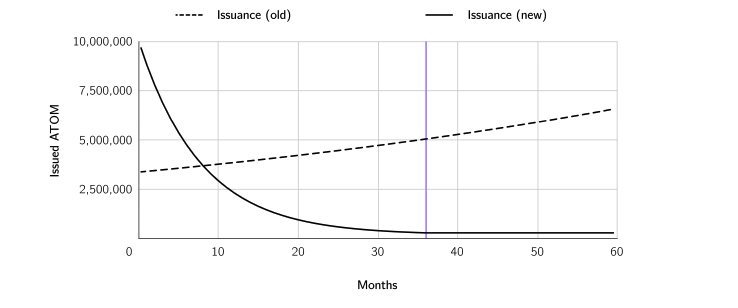
In this transition phase, there will be 10 million new ATOMs every month which will continue to decline for up to 36 months. After 36 months, ATOM will enter a stable phase where the number of printing will drop drastically to 300,000 ATOM per month.
Interchain Scheduler & Allocator
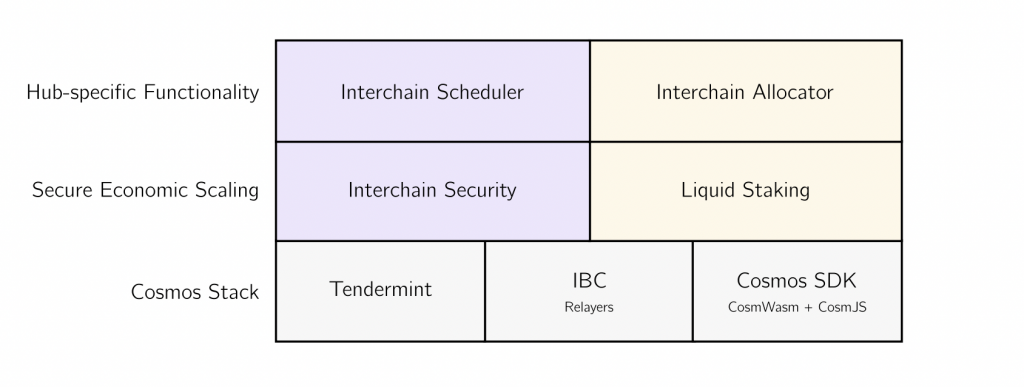
The Cosmos ecosystem, like any other blockchain, has its own Maximal Extractable Value or MEV problem. MEV is a group of people who use computer algorithms to look for potential arbitrage profits from price differences (through rearranging, reorganizing, and prioritizing block space). In fact, on the Osmosis platform, MEV managed to take a profit of $6.7 million US dollars. At its worst, MEV makes users have to pay a higher price when buying assets or paying transaction fees. On the plus side, MEV helps maintain price balance.
💡 Maximal Extractable Value or MEV is a phenomenon that has existed in the crypto industry since the beginning of Ethereum.
Cosmos is trying to solve the MEV problem using the interchain scheduler. Basically, the interchain scheduler creates an official marketplace for cross-chain MEV using the IBC protocol. This market for MEV provides validators and appchains with an attractive profit opportunity but does not compromise the network security and user experience of Cosmos.
The interchain allocator is a mechanism for allocating funds in the Cosmos Hub treasury to invest and fund new appchains through a voting system. The interchain allocator is a technological foundation so that the community of ATOM owners can support the development of the Cosmos ecosystem. In addition, the ATOM 2.0 whitepaper also provides a framework for appchains to work with Cosmos Hub to support each other through various incentive schemes.
Cosmos Ecosystem Management
Finally, in addition to the interchain allocator, Cosmos has also created a governance framework that focuses on the important role of all Cosmos ecosystem stakeholders, including ATOM owners. The Cosmos Councils and Assembly handle the governance system where stakeholders can manage various policies related to ATOM and Cosmos.
Cosmos Assembly is a collective community of interchain ecosystems from various stakeholders. It has the role of managing the Cosmos Hub treasury, allocating funds, and being the DAO representing Cosmos. On the other hand, the Cosmos Councils are the smaller entities that populate the Cosmos Assembly. It is a coalition of certain appchains and blockchains on Cosmos.
Difference between ATOM and ATOM 2.0
The upgrade brought by ATOM 2.0 will change the role of ATOM assets. The main thing about difference between ATOM and ATOM 2.0 is how ATOM takes advantage of the various appchains connected to the Cosmos Hub. If this update passes, ATOM will have essential connection to the developments of the interchain ecosystem. Not only that, ATOM will become the economic center of Cosmos through interchain security, liquid staking, and a new interchain governance mechanism.
In addition, the new ATOM tokenomics will have a positive impact in the long term. With printing down to 300,000 ATOM per month, this will reduce selling pressure significantly.
💡 In the new Whitepaper, the team’s vision of the Cosmos hub are the following: “the Cosmos Hub will become a self-propagating economic engine that drives the expansion and integration of the Cosmos Network.”
Analysis of Cosmos Update
The various updates described by the Cosmos development team must be very interesting, right? For those of you who own ATOM, the Cosmos update and ATOM 2.0 provide a lot of hope for the future of the interchain ecosystem. For starters, these changes provide many new uses for the ATOM token. It also transformed Cosmos Hub which was previously only an interoperability provider (via IBC), into an active player that is important for the development of the interchain ecosystem.
However, as with all analyses, we should look at the Cosmos upgrade with a degree of pessimism. This is useful so that we remain critical in seeing the potential of ATOM. The first thing we need to note is that this major update has a three-year implementation roadmap. Even the earliest version of the interchain security feature will only launch on Q1 2023. In addition, the Cosmos team will face various technological obstacles in its implementation. Reflecting on the update of The Ethereum Merge, it is not impossible that Cosmos also experience some kind of delays.
Another concern regarding ATOM 2.0 is the impact of printing the new ATOM in the short term. As explained in the whitepaper, ATOM’s printing will initially increase to 10 million per month. This printing is done as a subsidy and incentive. While this number will continue to decrease, it is still a large number. Meanwhile, ATOM issuance now is about one million every month from block rewards. So, this will surely add selling pressure in the short term after the interchain security feature is released.
You can find out more about ATOM 2.0 upgrade straight from one of its founders, Ethan Buchman in the video below:
How to Buy ATOM at Pintu
You can start investing in ATOM tokens by buying them in the Pintu app. Here’s how to buy ATOM on the Pintu application:
- Create a Pintu account and follow the process of verifying your identity to start trading.
- On the homepage, click the deposit button and top up the Pintu balance using your preferred payment method.
- Go to the market page and look for the ATOM token.
- Click buy and fill in the amount you want.
- Now you have ATOM tokens!
In addition, the Pintu application is compatible with various popular digital wallets such as Metamask to facilitate your transactions. Come and download the Pintu cryptocurrency app on Play Store and App Store! Pintu is regulated and supervised by CoFTRA and Kominfo.
You can also learn more crypto through the various Door Academy articles which are updated every week! All Pintu Academy articles are for educational purposes, not financial advice.
References
- Kirill Naumov, Exploring the Cosmos | Galaxy — Engineering a new economic paradigm, Galaxy Research, accessed on 4 October 2022.
- Donovan Choy, Here Comes Cosmos 2.0, Bankless, accessed on 4 October 2022.
- PROPOSAL: A new vision for Cosmos Hub – Hub Proposals / Signaling/Text, Cosmos Hub Forum, accessed on 5 October 2022.
- The Cosmos Hub Roadmap 2.0, Cosmos Hub, accessed on 5 October 2022.
- Yun Heng Lin, ATOM Outperforms Major Layer-1s Amid Market Drawdown, Delphi Digital, accessed on 6 October 2022.
- Eshita Nandini, Analyst Note: Cosmos Hub V2 Proposal, Messari, accessed on 7 October 2022.
Share