What is Layer Zero?

Interoperability is one of the major issues in the crypto industry. Many development teams are creating protocols and blockchains that have built-in interoperability with various other networks. This is important so that users can move assets easily and securely. However, many of the bridging technologies that facilitate interoperability are increasingly being targeted by hackers and criminals. In recent years, hundreds of millions of US dollars have been lost by hackers taking advantage of bridge protocol weaknesses. One protocol that seeks to address the problems is Layer Zero. Instead of using existing bridge architectures, LZ innovates on interoperability technologies. So, what is Layer Zero? How does it work? This article will discuss it in detail.
Article Summary
- 📨 Layer Zero is a cross-chain messaging protocol designed to facilitate interactions between smart contracts across different blockchain networks. It aims to address interoperability issues in the crypto industry.
- ⚙️ The protocol has three main components: the Relayer, Oracle, and Endpoints. Furthermore, The protocol has been integrated with 26 blockchains and is used by various applications.
- ⚖️ LZ has several advantages over other cross-chain protocols, such as the ability to move native assets, simple and lightweight implementation, and a secure cross-chain system.
- 📱 Layer Zero also created two new token standards integrated into its network: Omnichain Fungible Token (OFT) and Omnichain Non-Fungible Token (ONFT).
What is Layer Zero?
Layer Zero is a cross-chain messaging protocol. ‘Message’ refers to the data sent, received, and generated from blockchain networks. Layer Zero facilitates interactions between smart contracts on different networks. The protocol is intentionally lightweight so that it can be integrated across different blockchain networks. The team can also easily modify the protocol to integrate new blockchain designs.
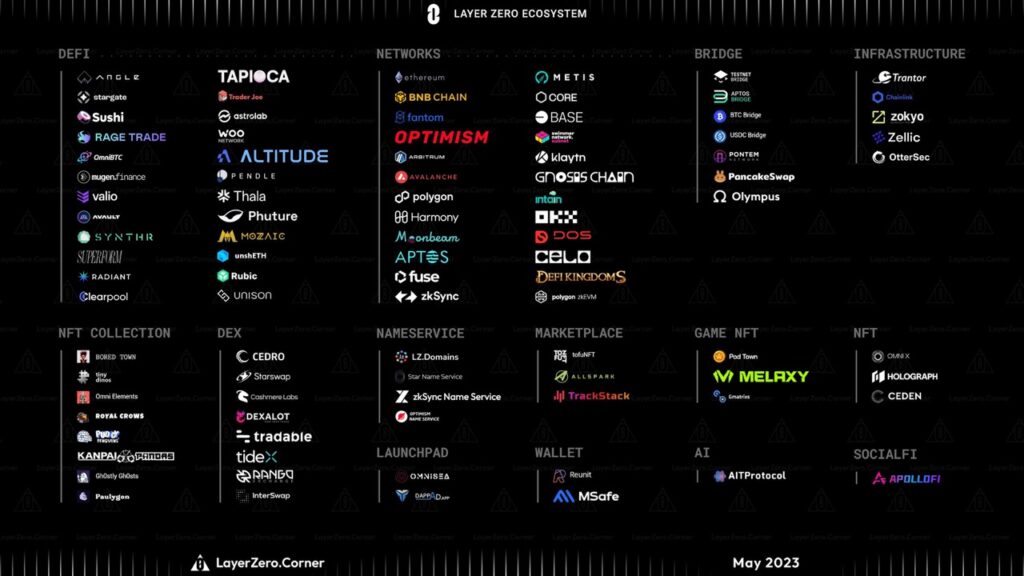
The messaging protocol runs using several components. These components are the off-chain oracle, off-chain relayer, and Endpoints attached to each blockchain. These three components allow applications to send data cross-chain. Since LZ operates simultaneously on multiple blockchains, it is an omnichain protocol.
Currently, LZ already connects to 26 blockchains and continues to develop new integrations. Many applications use Layer Zero to create liquidity and cross-chain DeFi activity. Examples of applications using LZ are Radiant Capital, Lybra Finance, Tofu NFT, and Trader Joe.
Who is the Founder of Layer Zero?
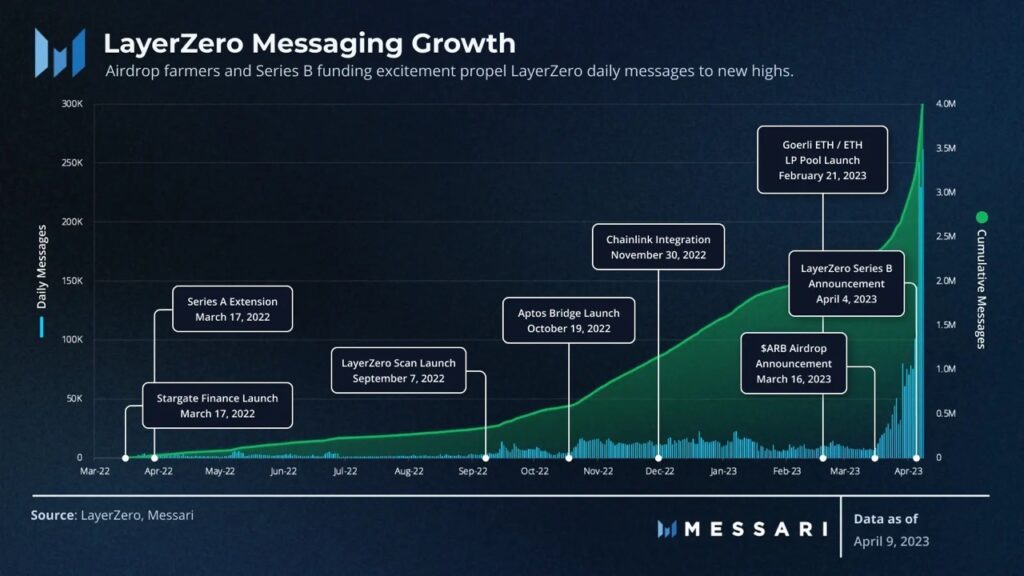
The protocol was developed and founded by Layer Zero Labs in September 2021. The development team announced its first fundraising in early 2022, along with the launch of the first Layer Zero protocol, Stargate Finance. So, in April 2023, Layer Zero raised $120 million dollars in Series B funding. The latest round raises the valuation of the Layer Zero protocol to $3 billion dollars. This is remarkable as this was achieved without any LZ tokens. So, talk of a token airdrop has been making the rounds on Twitter in recent months.
What Are the Advantages of Layer Zero Over Other Cross-Chain Protocols?
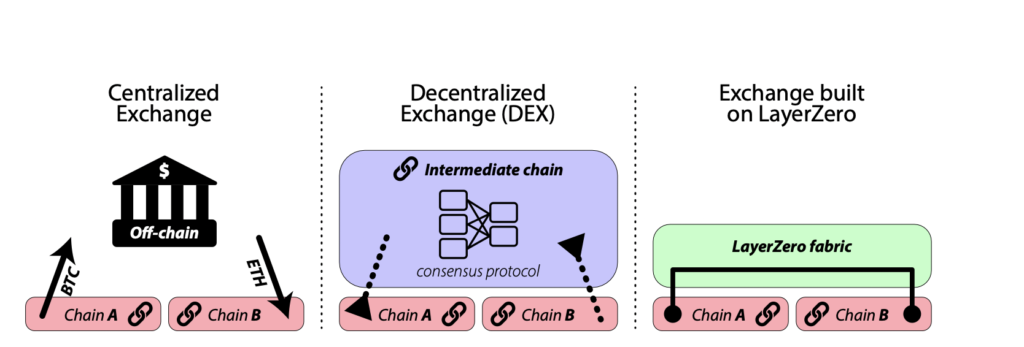
- Layer Zero Moves Native Assets: LZ does not move assets using wrapping or third-party systems. All assets that move through LZ are native.
- Easy Implementation: The protocol is lightweight so it is easily implemented by development teams. This is proven by more than 100 applications that are already using LZ.
- A secure cross-chain system: The protocol is a relatively new technology in the crypto world. However, the cross-chain system has never been hacked. This proves the safety of LZ’s cross-chain bridge system.
How Does Layer Zero Work?
Layer Zero’s technology is an important innovation. It is different from previous bridge technologies such as Wormhole. Instead of using a wrapping system to move assets, Layer Zero sends native assets by utilizing off-chain oracles and modules that can be used by blockchain and user applications. These modules are very lightweight and easy to upgrade.
Read the Layer Zero Whitepaper which you can access here.
As mentioned, the main components of the protocol are Relayer, Oracle, and Endpoints. Furthermore, Relayer and Oracle are independent entities. Since late November 2022, LZ has been working with Chainlink, the largest decentralized oracle in the crypto industry. Chainlink’s proven technology makes it the official oracle for Layer Zero (networks can still choose their own oracle).
Need to know what Chainlink is? Read the article about Chainlink at Pintu Academy!
Meanwhile, the relayer is an independent entity in charge of sending transaction proofs and transaction data from chain A to B. The relayer is also in charge of matching the block header hash from chain A to B. The main requirement for a successful transaction in Layer Zero is if the block headers and transaction proofs on chains A and B match. The protocol allows blockchains and users to use their own relayer. However, LZ also provides relayer services to blockchains and applications that want to use them.
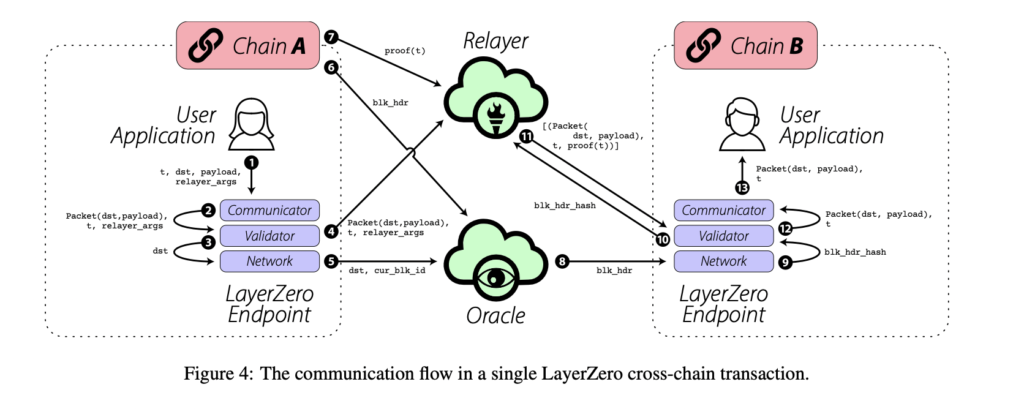
Finally, endpoints are an important component of every blockchain in Layer Zero. Endpoints are a group of smart contracts divided into four modules: Communicator, Validator, Network, and Libraries. Communicator, Validator, and Network are the main components of an endpoint.
Meanwhile, libraries are modules containing a suite of code for each blockchain network. If the protocol wants to add a new network, LZ only needs to add new codes to the libraries while the other components (communicator, validator, and network) stay the same. The current version of libraries is Ultra-Light Nodes.
Layer Zero's endpoints are modular. This means that LZ can update them easily. Recently Layer Zero collaborated with the PolyhedraZK team to create a ZK-based validator module for endpoints. So, applications can choose to submit transactions using ZK technology by simply integrating Layer Zero.
One of the reasons why the Layer Zero protocol is so easy to implement is that each endpoint has very lightweight modules. In addition, the relayer and oracle store all transaction data, not the blockchains. This makes Layer Zero less costly to implement, even on a network as expensive as Ethereum.
Layer Zero’s ONFT and OFT standards
In addition to the three important components above, Layer Zero has two standardized token formats. Omnichain Fungible Token or OFT is a token standard for the Layer Zero protocol. OFT V1 can only work on EVM blockchains while OFT V2 can work on non-EVM networks. Developers can directly convert their tokens to OFTV2 by adding the ProxyOFTV2.sol extension.
Meanwhile, Omnichain Non-Fungible Token or ONFT is an NFT token standard that can utilize the Layer Zero protocol. Like the token standard on Ethereum, ONFT has two versions, ONFT721 and ONFT1155.
Layer Zero weakness: UniSwap released a report on the bridge criteria it will use for users. In the report, LZ has not met the decentralization criteria and UniSwap is waiting for upgrades from the LZ team.
Will Layer Zero Airdrop Its Token?
Over the past few months, rumors have spread that Layer Zero token will be airdropped in the near future. This has led to many people looking for ways to qualify for an airdrop based on the criteria previously used by the Arbitrum and Optimism dev teams.
Here are some threads on Twitter that you can use to find ways to get Layer Zero token airdrop:
- Stacy Muur on Twitter: “The LayerZero snapshot is almost here, and the $ZRO token launch is just months away. I’ve got your back with a FREE INTERACTIVE dashboard.”
- Leshka.eth ⛩ on Twitter: “🧵 Last chance to get Layer Zero #airdrop. I’ve compiled the best existing strategies.”
- zucl1ck on Twitter: “Want to unlock a potential airdrop of $3,000+? Discover the secret to making 100 transactions for only $2 on LayerZero.”
Conclusion
Interoperability is a major challenge in the crypto industry and the technology is a prime target for hacking. So, Layer Zero creates a cross-chain messaging protocol that enables interaction between smart contracts on various blockchains. Layer Zero has advantages such as native asset delivery, uncomplicated implementation, and a secure cross-chain system. Layer Zero relies on three main components namely Relayer, Oracle, and Endpoints.
Currently, the LZ ecosystem consists of 26 blockchains and DeFi applications use LZ to create cross-chain liquidity and DeFi activities. Layer Zero also offers two standardized formats for tokens, namely Omnichain Fungible Token (OFT) and Omnichain Non-Fungible Token (ONFT).
How to Buy Cryptocurrency in Pintu
Start investing in cryptocurrencies by buying them on the Pintu app. Here is how to buy crypto on Pintu:
- Create a Pintu account and follow the process of verifying your identity to start trading.
- On the homepage, click the deposit button and top up the Pintu balance using your preferred payment method.
- Go to the market page and look for your favorite crypto (like BTC).
- Click buy and fill in the amount you want.
- Now you are a crypto investor!
In addition, the Pintu application is compatible with various popular digital wallets such as Metamask to facilitate your transactions. Go and download the Pintu cryptocurrency app on Play Store and App Store! Pintu is regulated and supervised by Bappebti and Kominfo.
You can also learn crypto through the various Pintu Academy articles which are updated every week! All Pintu Academy articles are for educational purposes, not financial advice.
References
- 🐍Salazar.eth 🦇🔊 on Twitter: “Recently Layer Zero closed a second funding round for $120M at a $3B valuation from the top VC firms”, Twitter, diakses pada 14 Juni 2023.
- What is LayerZero – LayerZero Docs, diakses pada 15 Juni 2023.
- Chase Devens, Inside LayerZero’s $120M Series B Raise: How the Cross-Chain Protocol is Driving Growth, Messari, diakses pada 15 Juni 2023.
- Revelo Intel, What You Need to Know About LayerZero, Substack, diakses pada 16 Juni 2023.
Share