What is Crypto Validator, and Is It Still Profitable?
Validator in the crypto world plays an important role in ensuring that transactions on a blockchain network running smoothly and securely. Although it can be a lucrative source of income, becoming a validator requires specialized knowledge and significant investment in both crypto assets and hardware and software. This article discusses the role of crypto validators, the advantages, risks, and the steps required to become one.
Article Summary
- 🔎 A crypto validator is a participant on a Proof-of-Stake (PoS) blockchain whose job is to validate transactions on the network for rewards.
- Crypto validators are necessary for the blockchain ecosystem. They are responsible for network security, transaction validation, and consensus building.
- ⚖️ The work of a validator can be simplified into three steps: selecting a blockchain network, choosing the right software and hardware, and running the nodes according to the requirements specified in the blockchain protocol.
- ⚠️ There are risks that validators face: slashing, high fees, and liquidity risk as tokens are locked.
What is Crypto Validator?
A crypto validator is a participant on a Proof-of-Stake (PoS) blockchain whose job is to validate transactions on the network for rewards. These validators will determine whether a transaction is valid or not. When a transaction is deemed valid, they add it to the ledger. That way, a network can ensure its integrity and security.
Although both are tasked with validating blockchain transactions, validators are not the same as miners. The main difference lies in the consensus mechanism. Validators work on a Proof-of-Stake (PoS) mechanism, while miners work on a Proof-of-Work (PoW) mechanism.
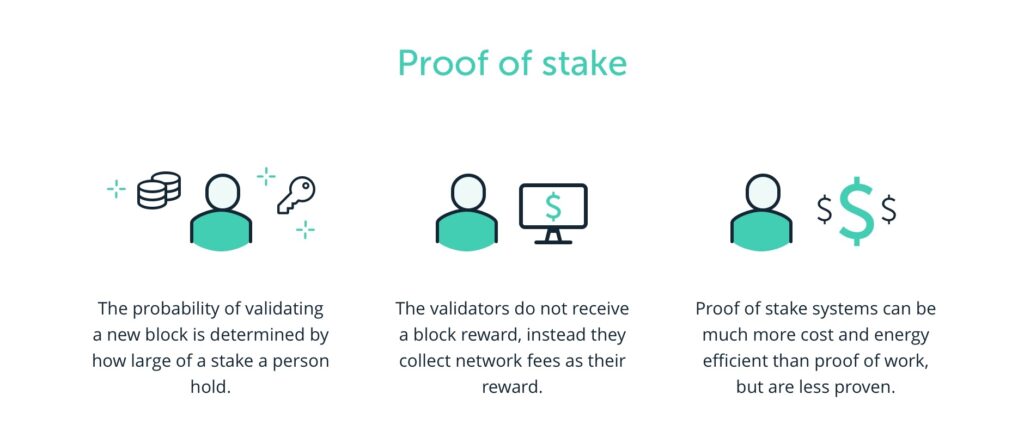
In PoW, miners must use mining rigs such as Application Specific Integrated Circuit (ASIC) to validate transactions. ASIC is a supercomputer device that is expensive and has a high level of energy consumption. In PoS, to validate transactions, validators simply stake some crypto assets to get the opportunity to be selected as a validator. The computer used also does not need to be as sophisticated as ASIC. The amount that must be staked will vary depending on the crypto asset itself.
Want to know more about the PoW mechanism used in Bitcoin? Read the full explanation in the following article.
Why Crypto Validator Needed?
The following are the reasons why crypto validators necessary in the blockchain ecosystem:
- Transaction validation. Crypto validators are responsible for validating transactions on the blockchain. The validators ensure that each transaction follows the rules of the protocol.
- Consensus building. Crypto validators are also used to build consensus on a blockchain. With the validators reaching a consensus, it will ensure the blockchain remains intact and functional.
- Network security. Crypto validators play an important role in blockchain security. They prevent fraudulent transactions from being added to the blockchain, thus ensuring the integrity and security of a blockchain.
How Crypto Validators Work
Explaining how a validator works is quite complex, given that each blockchain’s mechanisms can differ. However, the workings of a validator can be simplified into three steps: choosing a blockchain network, selecting the right software and hardware, and running the nodes according to the blockchain requirements.
Setting up the software and hardware is relatively easy, as guides are available to help you. However, running the nodes, in the long run, is the tricky part. You need at least some knowledge and understanding of the technical aspects of computer networks, cybersecurity, troubleshooting, and blockchain protocol.
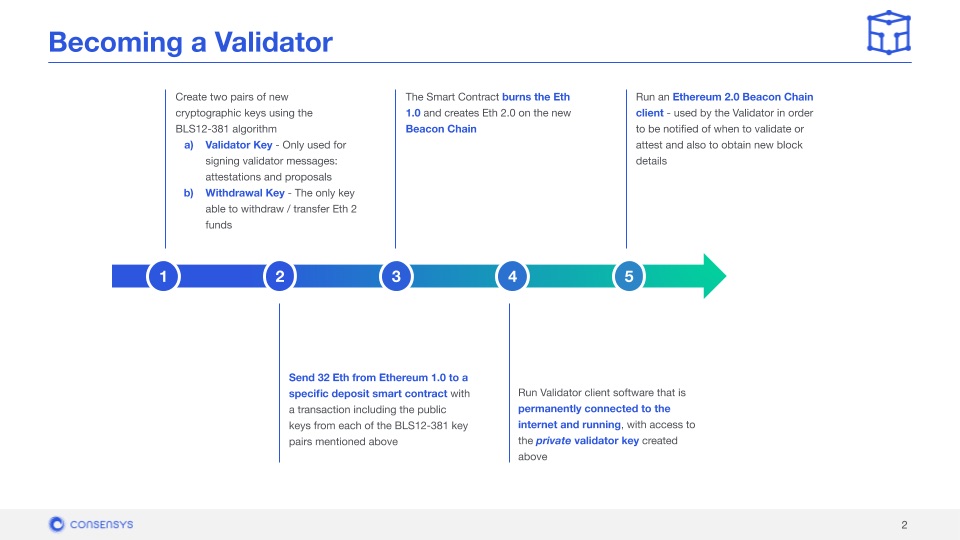
When verifying, validators will run specialized software to communicate with other nodes in the network. This is to ensure that every transaction is valid and follows the rules. They are also responsible for storing transaction data, processing and verifying transactions, and adding new blocks to the blockchain.
By performing all of these tasks, validators are rewarded in return. However, if validators do not function optimally, they can be penalized. The penalties can range from having their staked assets deducted to having their position as a validator revoked and not being able to register as a validator again.
You can learn more about staking and how it works in the following article.
How to Become A Crypto Validator
For those of you who want to become a validator, it is mandatory to prepare supporting hardware and software and have some crypto assets to be staked. Each protocol and crypto asset has its own requirements that must be met
The following document shows the minimum hardware specifications to become a validator on the Ethereum network. Meanwhile, this document contains the steps that Ethereum validators must take. Below are the requirements and steps to become a validator on various protocol networks:
| Network | Processor | Memory | Storage | Total Validators | Required Minimum Stake | Reward Rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ethereum | 4+ cores @ 2.8+ GHz | 16GB+ RAM | 2TB SSD | 556.622 | 32 ETH | 4,58% |
| Solana | 12 cores @ 2.8+ GHz | 128GB+ RAM | 1TB SSD | 1.639 | 1 SOL | 7,7% |
| Avalanche | 8 cores @ 2.8+ GHz | 16GB+ RAM | 1TB SSD | 1.262 | 2.000 AVAX | 9,51% |
| Polkadot | 4+ cores @ 3.4+ GHz | 16GB+ RAM | 1TB SSD | 297 | 350 DOT | 15,32% |
| Polygon | 8 cores @ 2.8+ GHz | 32GB+ RAM | 2,5TB SSD | 100 | 1 MATIC | 10,01% |
For example, to become a validator on the Ethereum network, staking of 32 ETH is required. In becoming an Ethereum validator, there are various ways you can choose. You can do it by solo staking, where you fully participate by performing various validator tasks and locking in 32 ETH.
There is also staking as a service, where you assign another party to handle the technical aspects. So, you only need to prepare 32 ETH to stake, while the staking service will do the rest. Another way to become a validator on the ETH network is through pooled staking. Liquid staking platforms can be an option for those not comfortable entirely staking 32 ETH.
Remember, by becoming a validator on the Ethereum network, the 32 ETH you stake, and its rewards will be locked indefinitely. You can only stake out the assets and profits when Ethereum has completed the Shanghai Upgrade.
Pintu Academy has written about the Shanghai upgrade and its various updates in the following article.
Crypto Validator Reward
Rewards for crypto validators vary as they depend on each crypto protocol. Also, the time of reward distribution might differ for each protocol. In the PoS mechanism, the rewards earned by validators will be based on per epoch. Generally, one epoch is between 1-3 days. The number of rewards received and the distribution period can usually be found on each protocol’s website.
However, you can use validator reward calculator websites to get an idea of the rewards earned by validators. For example, through the Stakingrewards website, you can calculate the potential rewards of various protocols. You only need to enter the number of crypto assets staked, the asset lock period, the type of validator, and the assumed crypto price.
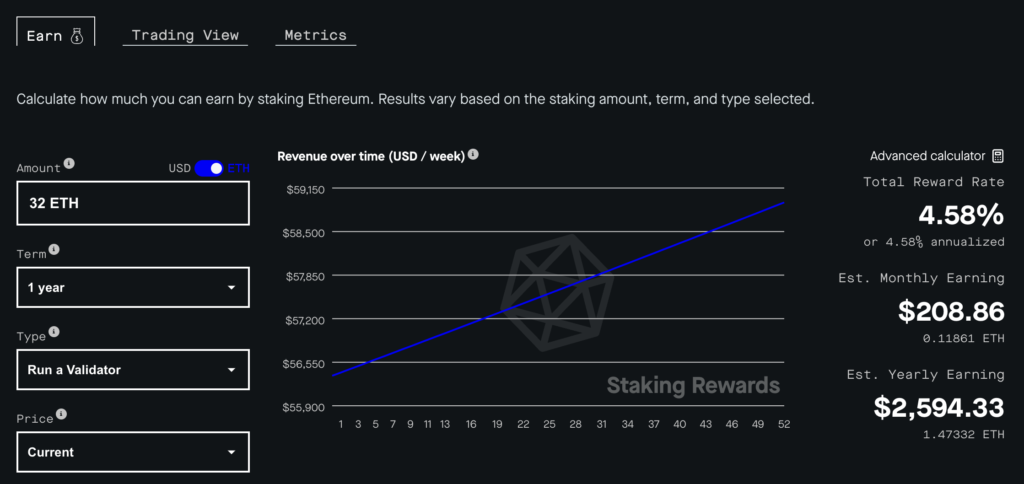
Based on the example above, if you become a solo validator on the Ethereum network, the estimated income earned is 4.58% a year. This means that by staking 32 ETH, the validator will earn around US$ 2,594.33 per year, assuming the ETH price is at US$ 1,700. However, keep in mind that the simulation is only an example. Given the volatile asset prices, the calculation will likely differ in real-time.
Crypto Validator Risk
Being a validator comes with some risks that you need to be aware of:
- Slashing. When becoming a validator, there is a risk of being partially or fully slashed if you do not perform your duties properly. Slashing occurs when two different blocks are signed for the same slots, when validators contradict each other, or when they sign two simultaneously to initiate a validation. If slashed, the value of the validator’s staked assets will be deducted depending on the mistake.
- Liquidity. To become a validator, each user must stake an asset for a certain period. This makes the asset inaccessible until the lock period ends. Consequently, users cannot sell their assets when their value has decreased or increased sharply.
- Costs. Being a validator is not as expensive as being a miner, but it still costs a lot of money. The capital required for hardware staking can reach hundreds to thousands of US dollars. Not to mention the need for electricity and internet costs.
Conclusion
In conclusion, becoming a crypto validator can be a rewarding experience. Validators play a vital role in maintaining the security and integrity of blockchain networks, and their participation is essential for the success of these networks. However, becoming a validator requires a significant investment of time, money, and effort, and it is not without its risks. If you are considering becoming a validator, it is essential to do your research and understand the technical and financial requirements involved. With the right knowledge and preparation, becoming a validator can be a fulfilling and profitable venture.
Buy Crypto Assets in Pintu
Interested in investing in crypto assets? Take it easy, you can buy various crypto assets such as BTC, ETH, SOL, and others safely and easily. Furthermore, Pintu has subjected all its crypto assets to a thorough evaluation process, emphasizing the importance of prudence.
Pintu is also compatible with popular wallets such as Metamask to facilitate your transactions. Download Pintu app on Play Store and App Store! Your security is guaranteed because Pintu is regulated and supervised by Bappebti and Kominfo.
In addition to executing transactions, in the Pintu Apps, you can also learn more about crypto through various Pintu Academy articles updated weekly! All Pintu Academy articles are made for knowledge and educational purposes, not as financial advice.
Reference
Ethereum, What is Validator? accessed on 24 March 2023.
Alexandria, What is Validator, Coin Market Cap, accessed on 24 March 2023.
Coin Telegraph, Ethereum 2.0 staking: A beginner’s guide on how to stake ETH, accessed on 24 March 2023.
Katie Rees, How Much Money Can You Make as a Crypto Validator? Make Use Of, accessed on 24 March 2023.
Lyle Daly, What Is Proof of Stake (PoS) in Crypto? The Motley Fool, accessed on 24 March 2023.
World Coin, Crypto Staking: A Beginner’s Guide, accessed on 24 March 2023.
Darry Port, Make Passive Income as a Crypto Validator On These 5 Blockchains. Money Made, accessed on 27 March 2023
Share