What Is SegWit (Segregated Witness) in Bitcoin?
In 2017, the bitcoin transaction fees that users had to pay to miners were very high. It slowed down bitcoin adoption and was the reason behind the proposed update called SegWit. What is SegWit? And how does it work? We will discuss this further in this article.
Article Summary
📜 SegWit is an update to the Bitcoin network to reduce the weight of transactions in a block on the blockchain.
💾 SegWit frees up space or block capacity on the Bitcoin network to accommodate more transactions.
Why SegWit?
In 2017, bitcoin users had to pay quite high transaction fees to the miners to validate transactions. This high fee was caused by the size of each Bitcoin block that was only 1 MB, while everyone who transacted with bitcoin wanted the transaction to be processed immediately and fought over the space.
In order for transactions to be included in the block, miners will prioritize transactions based on fees submitted by users. Each transaction also has its own amount of data. The more data that is used, the fewer transactions that can be included in the block. The fewer transactions that can be processed, the higher the cost to the miners because everyone is fighting for space in the block.
Because Bitcoin blocks are limited the fees paid to miners are getting more and more expensive. This raises concerns that fewer people will want to transact using Bitcoin because the fees are very expensive. Ultimately this problem will slow down Bitcoin adoption. Therefore we need a solution to overcome the problem of Bitcoin scalability, and one of these solutions is Segwit.
Read also: How Blockchain Works?
What is SegWit Bitcoin?
SegWit is an update of Bitcoin to reduce the weight of transactions in a single block blockchain implemented. SegWit, which stands for Segregated Witness, is basically a process where the block size limit on the blockchain is increased by removing the signature data from the transactions included in each block. This process will free up space or capacity so that the block can accommodate more transactions.
Launched in August 2017, this update separates the transaction into two parts. The first part contains data on the wallet addresses of the sender and recipient, and the second part contains “witness data” which contains the transaction signature.
Before SegWit, this digital signature or “witness data” was included in the block. However, this creates problems if someone wants to change the transaction ID to already spent, before the transaction is confirmed by the network. Those with malicious intent can pretend that this transaction didn’t happen, which may be useful for someone who wants to claim that they sent coins to someone else when they really didn’t.
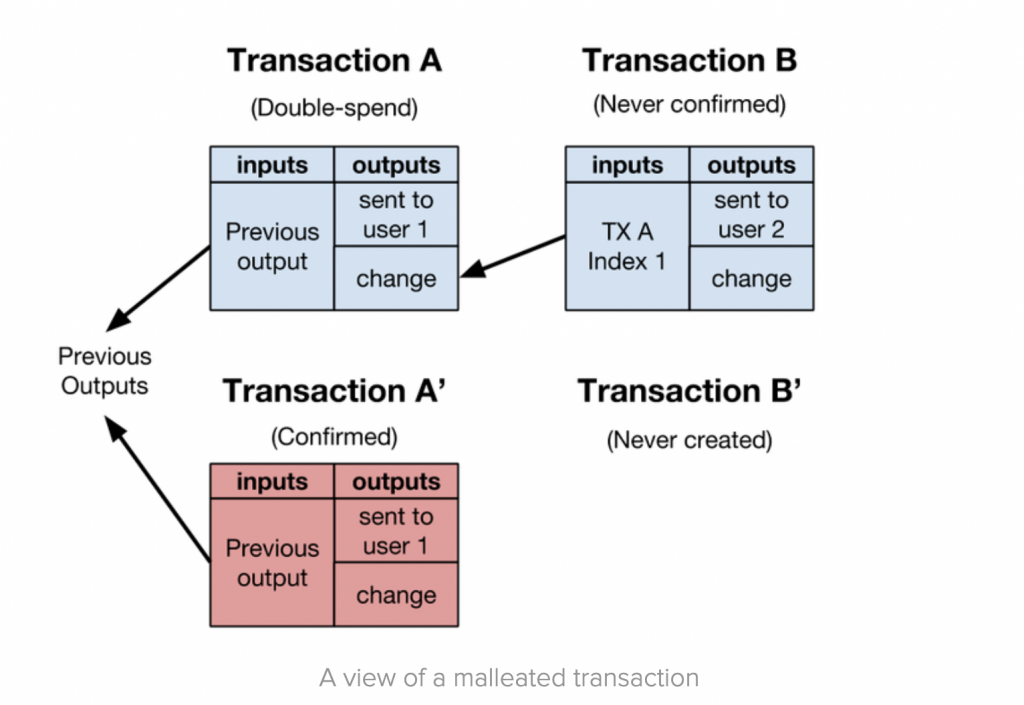
Prior to SegWit, witness data or digital signatures were one of the data entered into transactions. The Transaction ID of a transaction can be changed by manipulating the transaction opening code (your digital signature). Once you digitally sign a transaction, it is sent via Bitcoin’s cryptographic hash function which generates a unique transaction ID. If one character is changed in the digital signature, it will result in a completely different transaction ID.
SegWit moves the signature to the end of the transaction data, so a Transaction ID is created from everything except the digital signature. With SegWit this digital signature is separated from the block and cannot be changed thus fixing this issue. Because this signature data is separated from the block so there is more room for processing transactions.
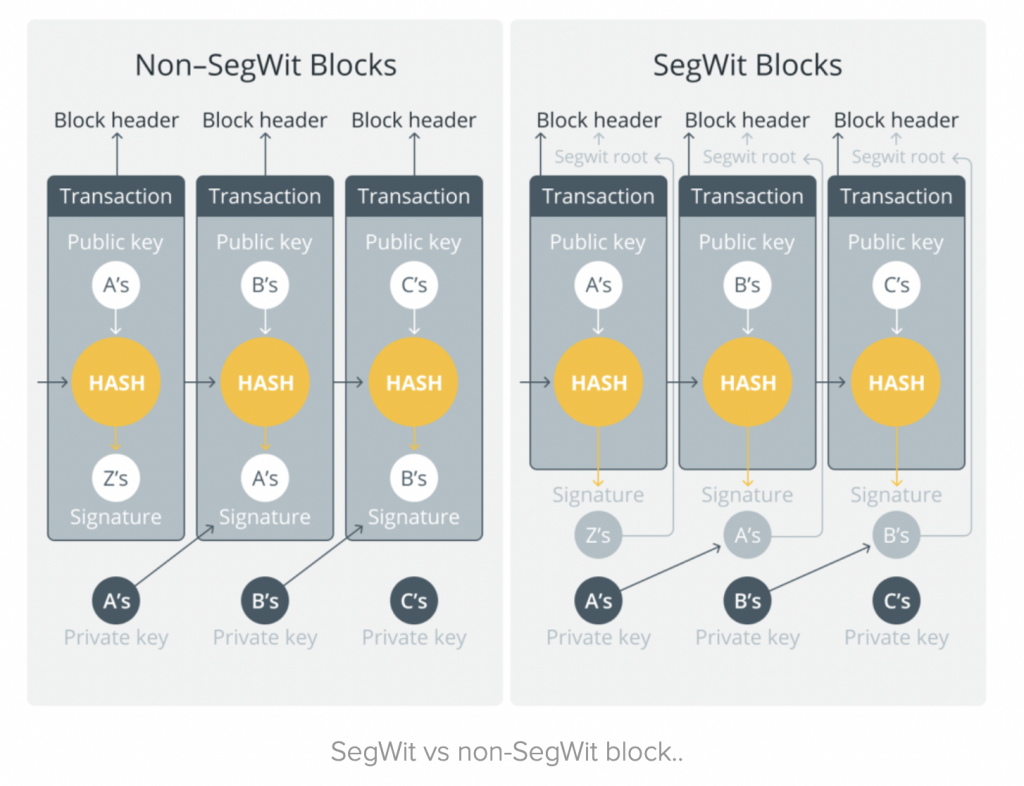
This splitting of witness data creates more space and allows more transactions to be included in the block thereby reducing fees for miners and increasing Bitcoin adoption.
What are the advantages of SegWit?
Is transaction with SegWit faster than legacy? With the existence of Segwit, where “witness data” or digital signatures are not included in the block, effectively after this “witness data” is deleted, it reduces 47% of the data used in the block. Thus there is 47% extra space to accommodate more transactions in the block. Because this extra space makes more transactions that can be accommodated in the block so that fewer transactions are queued in the mempool. So we can say that SegWit allows faster transactions confirmation.
SegWit is also a soft fork so that the protocol continues to run without breaking the existing consensus rules.
SegWit will also benefit holders of full nodes, as it can reduce the amount of data required to be stored on hard drives. In other words, Segregated Witness will reduce the requirement to run a full node and the time it takes to synchronize with the network.
SegWit adoption challenge
When the SegWit update was carried out there were other solutions offered to overcome Bitcoin scalability problems. These include Segwit2X which wants the bitcoin block to be 2x larger, from 1MB to 2MB, or even a hard fork that produces Bitcoin Cash, which wants the block size to be enlarged from 1MB to 8MB.
This debate is a challenge for the Bitcoin community because without Satoshi Nakamoto, the community also has different ideas about how to increase Bitcoin’s scalability. When SegWit2X was planned, there was a lot of opposition from developers, nodes, and miners. Meanwhile, those who support SegWit2X are the big exchanges like Coinbase.
Opponents of SegWit2X argue that by increasing block capacity it will become increasingly difficult to run nodes on their own so bitcoin does not become truly decentralized. Meanwhile, supporters of SegWit2X, who are mostly big exchanges, think that the more transactions they can do, the more profit they can get from the transaction fees received by exchanges. In 2017, the SegWit2X proposal was finally discontinued due to the overwhelming resistance from the Bitcoin community.
SegWit’s current state
Currently, SegWit adoption is at 82%. This adoption is also supported by the many wallet and hardware wallet applications that use SegWit addresses.
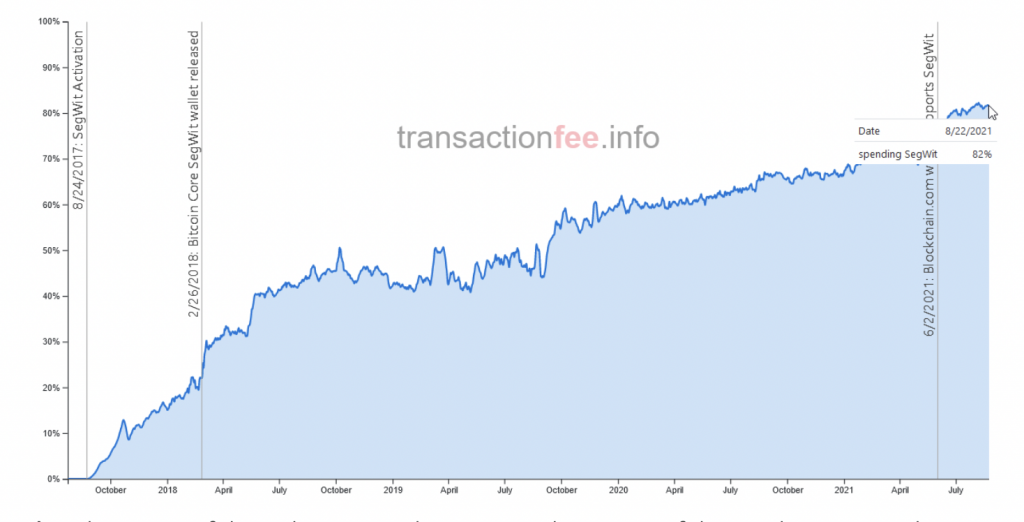
Until now users can still use the old address and SegWit address. SegWit address can send bitcoin to legacy address.
The old address or what is referred to as legacy uses the P2PKH (Pay to PubKey Hash) format. The difference between segwit and legacy address is below:
- Examples of Legacy Addresses are addresses that begin with the number 1 for example 1BvBMSEYstWetqTFn5Au4m4GFg7xJaNVN2.
- Or use P2SH (Pay to Script Hash) starting with the number 3, for example 3J98t1WpEZ73CNmQviecrnyiWrnqRhWNLy.
- While the SegWit address uses the Bech32 format starting with the letter bc1.. for example bc1q8fetux994vngxul7wftnfkv5aksvktf2they73
Changes after SegWit
SegWit is also the cornerstone of the development of the Lightning Network. By eliminating the possibility of changing transactions, a secure payment channel can be created that allows the Bitcoin network to process millions of transactions per second.
Read also: Bitcoin’s Lightning Network: Definition and How it Works
Currently, there has also been a Taproot update with different functions and minimizing transaction data. So the bitcoin block can process even more transactions. Which you can read in the description about Taproot.
Share


