What is Layer 2 Crypto?

Ethereum is one of the most popular blockchains in the crypto industry. It was also the “OG”blockchain to implement Smart Contracts that gave birth to the NFT and Defi sectors. As its user increases, the weaknesses of the network are becoming more and more apparent. Ethereum lacks sufficient scalability and network congestion causes transaction costs to reach hundreds of US dollars. Layer 2 technology was invented to solve the problem of scalability and expensive gas. So, what is Layer 2 Crypto? How did it solve the Ethereum scalability problem? This article will discuss layer 2 crypto on the Ethereum network.
Article Summary
- ⚖️ Layer 2 is a separate blockchain built on a layer 1 blockchain to overcome the problem of network scalability. The function of Layer 2 is to speed up the transaction process, reduce transaction costs, and provide an alternative network with expanded use cases.
- 🧠 The most popular scaling method in the L2 sector is rollup that “rolls”a group of transactions into a piece of data that can be easily processed by L1. In rollup, there are two variations, optimistic rollup, and zero-knowledge rollup.
- 🚧 Several L2 projects that use optimistic rollup are arbitrum, optimism, and Boba Network.
- 🏛️ Examples of L2 projects that use ZK are Loopring, Immutable X, and Aztec network. Beyond that, several crypto projects are developing ZK implementations such as Polygon, zkSync, StarkEx, and StarkNet.
- ⏳ The year 2023 will be an essential year for the development of L2. Arbitrum and optimism’s rollup technology continues to grow and both are able to capture a large portion of Ethereum’s market. Besides that, Polygon successfully collaborates with various large brands that managed to place it as the most dominant L2. Ethereum’s upgrade in 2023 will also benefit the L2 project on it.
What is Layer 2?
Layer 2 is a separate blockchain built on the Layer 1 blockchain to overcome network scalability problems. Layer 2 technology is born on the Ethereum network and is made because of the increasingly expensive Ethereum transaction fees and the slow transaction process (Ethereum transaction costs reach $190 in the last bull run). So, layer 2 is to speed up the transaction process, reduce transaction costs, and provide expanded use cases. The existence of layer 2 also reduces the load of the Layer 1 transaction because network users are naturally divided.
One crucial aspect that becomes the advantage of layer 2 is that it still utilizes the security of Layer 1. So, L2 still enjoys the high level of security provided by Ethereum. This is one of the main reasons why the L2 sector in Ethereum is popular.
The difference between layer 1 and layer 2 crypto lies in the network infrastructure. Blockchain layer 1 has complete infrastructure, data, network, consensus, and application layers. Meanwhile, Blockchain Layer 2 only has an application layer. It utilizes other layers from the L1 that it is built on.
Furthermore, developers realize that demand for applications in Ethereum remains high and Ethereum has not been able to meet said demand. This encourages the rapid development of its L2 sectors. At present, the layer 2 sector is especially useful for DeFi, NFT, and crypto-based games. Some examples of crypto layer 2 projects are Polygon, Arbitrum, Loopring, Immutable X, and Optimism.
The video below can give you a further explanation of the function of L2.
Advantages of Layer 2
- ⚡ Transaction speed and fees: L2 is designed to have better transaction speed and fees than layer 1. In fact, some layer 2 on Ethereum have transaction fees that are 10x cheaper than Ethereum.
- 🔒 Security of L1: As already explained, the main advantage of layer 2 is that it still takes advantage of the security that layer 1 has. This is the main reason why layer 2 still has many users compared to many other layer 1s.
- 🧠 Broader use cases: With faster transactions and much lower transaction fees, L2 opens up a variety of new use cases. Applications that were previously limited by Ethereum network congestion (such as trading applications GMX) can now choose to build on layer 2 that can meet their needs.
How Layer 2 Works
The L2 blockchain works in parallel and is an extension of the L1 underneath it. There are 2 possible pathways for L2 transactions, they can first process the transactions off-chain and then return them to Ethereum or do everything on-chain using novel technologies. In this way, the heaviest work is done by layer 2 so that the L! only plays a role in the final validation stage.
The essence of this process is how layer 2 can still take advantage of the security provided by layer 1 without using its costly transaction verification process. L2 allows layer 1 to handle security, data availability, and decentralization, while layer 2 handles transaction scaling. Ethereum itself openly supports layer 2 development as a scalability solution that does not compromise decentralization and network security.
The layer 2 concept is closely related to blockchain trilemma. What is the trilemma blockchain? Read here.
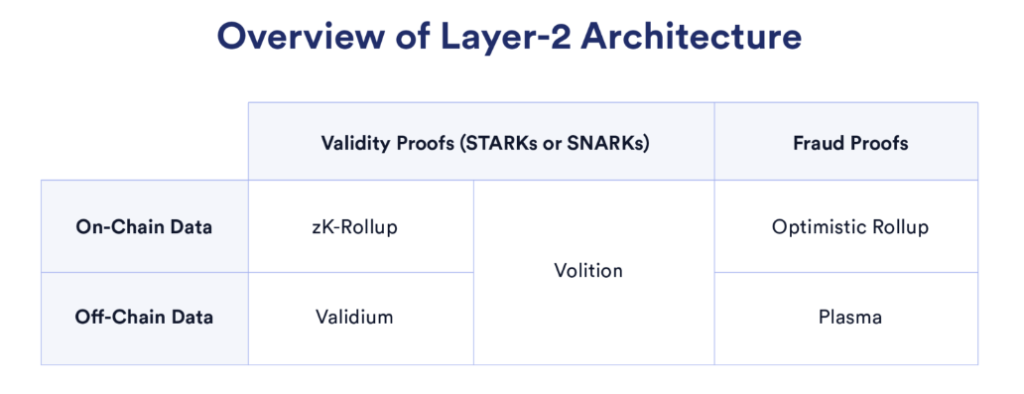
The way each layer 2 processes transactions is different and can be divided into several categories. Currently, the most popular method at layer 2 is rollup which batches (or rolling up) a group of transactions. Then, the batches of transactions are sent back to Ethereum as a piece of data that can be processed quickly. Within the rollup method, there are two variations, namely Optimistic Rollup and Zero-Knowledge (ZK) rollup.
Optimistic Rollup
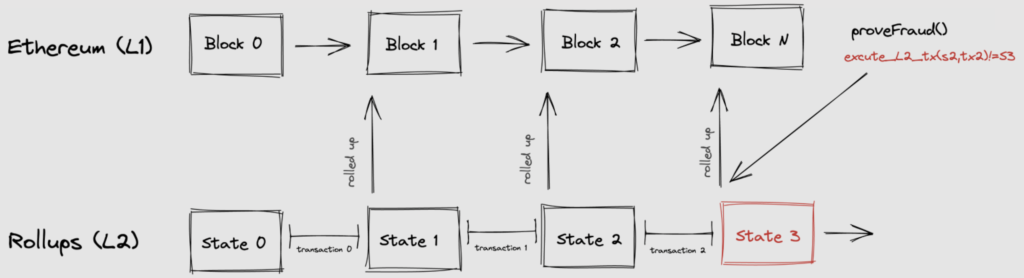
Optimistic Rollup is a layer 2 technology that rolls up transactions into a scrap of data which will then be processed by layer 1 such as Ethereum. All transactions that enter the rollup are considered valid (this is the reason they are called optimistic). The roll-up process occurs off-chain that runs parallel to layer 1.
Each Optimistic rollup uses fraud-proof which examines each set of transactions and looks for erroneous or potentially malicious transactions. Fraud proof has a dispute time delay (DTD) of 7 days to check which transactions are potentially problematic. Fraud proof can be uploaded to the network during the DTD period if a transaction is considered invalid or malicious. So, fraud-proof does not disrupt the network operations because it runs on top of EVM and can be resolved quickly.
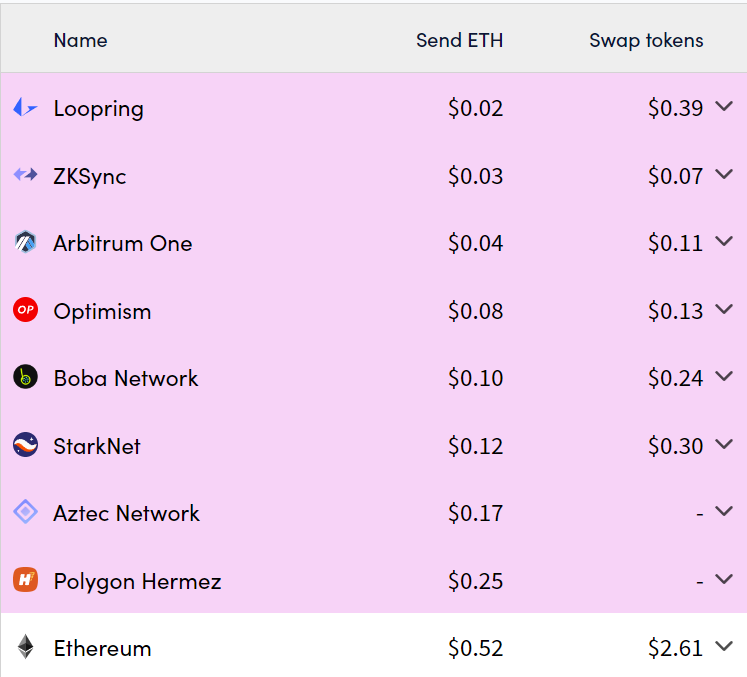
Optimistic Rollup saves transaction costs and accelerates the transaction validation process because it complies hundreds of transactions into a piece of data. The rollup process avoids the Ethereum network congestion because it utilizes off-chain networks. As in the picture above, layer 2 which uses Optimistic Rollup (optimism and arbitrum) has a transaction fee that is 10x cheaper than Ethereum.
However, one of the biggest weaknesses of using optimistic rollup is the time period for withdrawing assets from the blockchain. This is related to 7 days DTD from Fraud Proof which must check transactions before the withdrawal is successful. Arbitrum and optimism require up to one week before the user’s funds can be withdrawn from the network.
Below is a simple table for comparing Optimistic Rollup and ZK-Rollup.
| Optimistic Rollup | ZK-Rollup | |
|---|---|---|
| Withdrawing Assets | A few days | Minutes to hours |
| EVM Compatibility | 100% compatible EVM | EVM implementation is still hard |
| Computational cost | Low | High |
| Technological complexity | Low | High |
| Types of proof | Fraud proofs | Validity proofs |
| Data compression | All transactions must be compressed in the rollup process | Only certain transactions need to be compressed |
Zero-Knowledge
Zero-Knowledge is the latest technology of Ethereum scalability that utilizes Validity Proof (ZK-Proof) that ensures transactions are valid. The basic concept of ZK is basically the same as a rollup in that batches a number of transactions and processes them, producing a ZKP that the L1 needs to add to the chain state. ZK also maintains the privacy of its transactions because the private data are not revealed (hence the name ‘zero knowledge’). Additionally, unlike rollups, ZK technology allows the withdrawal of funds to occur within minutes.
The pillar of this novel technology lies in ZK-Proof (ZKP) which can prove the validity of transactions without having to see the information within. There are two elements in producing ZKP: verifier and prover. Producing ZKP involves a complicated cryptographic process and requires high computing power.
In addition, ZK technology as layer 2 Ethereum also has several variations based on the ZKP type (interactive and non-interactive). Interactive ZKP requires the prover to prove the validity of transactions to several verifiers while non-interactive ZKP can be verified by all verifiers in the same batch.
There are two types of ZKP, zk-SNARK (Succinct Non-Interractive Argument of Knowledge) and zk-STARK (Scalable Transparent Argument of Knowledge). Zk-STARK is trustless, safer, has higher scalability, and is more transparent than zk-SNARK. However, zk-STARK requires a larger ZKP size and the verification time is longer. Zk-SNARK is more efficient in using gas and faster at verifying transactions but requires trust at some level. At present, the development team of various ZK projects is still trying to reduce the difficulty of producing ZKP to make it viable.
Other layer 2 methods:
- Sidechain: Sidechain is L2 in the form of an independent blockchain that runs parallel with the main network of Ethereum. It is compatible with EVM but must utilize bridge technology to interact with the Ethereum mainnet. Therefore, Sidechain cannot take advantage of the security provided by Ethereum.
- Validium and Volition: Validium is a ZK technology that utilizes off-chain systems to store data so as to reduce gas costs and increase TPS. Like sidechain, validium does not take advantage of the security offered by layer 1. Meanwhile, volition allows users to choose between using ZK-Rollup or validium.
Layer-2 Projects
Polygon
Polygon (MATIC) is one of the most popular Ethereum L2 projects. Polygon’s main L2 is currently Polygon PoS, a unique sidechain that has its own consensus mechanism but still utilizes some Ethereum safety features. Polygon PoS has succeeded in processing 960 million transactions and already has 200 million users based on its total Unique Addresses. Polygon is also developing 4 other L2 solutions, with 3 of them utilizing ZK technology.
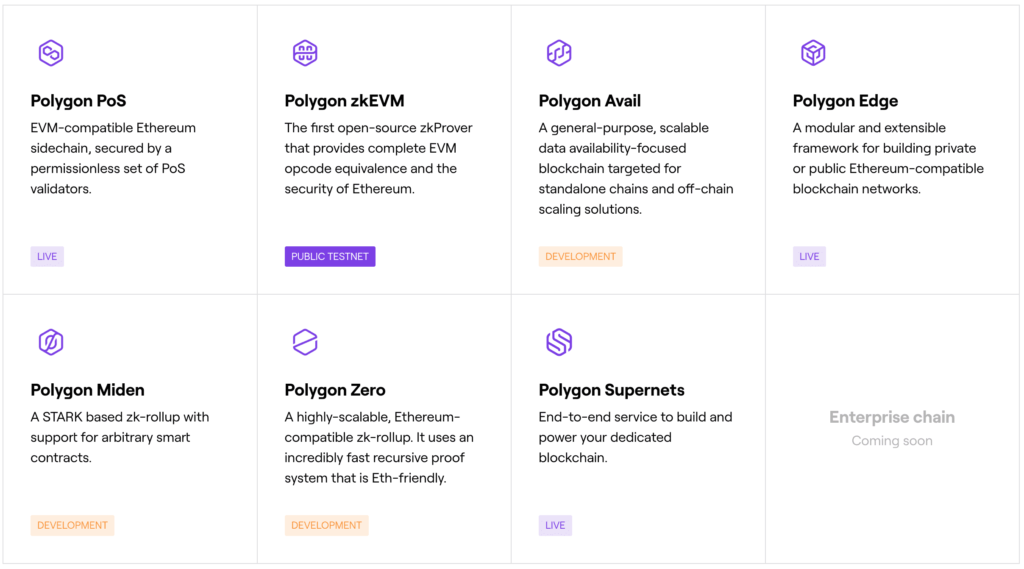
As in the picture above, there are 5 L2 solutions in the polygon ecosystem: Polygon PoS, zkEVM, Avail, Zero, and Miden. Polygon zkEVM, Zero, and Miden are Polygon’s efforts to enter the ZK sector. Among the three ZK projects, zkEVM is predicted to have the greatest potential. Polygon zkEVM is the only two ZK projects that aim to integrate zk with EVM (Ethereum Virtual Machine). Furthermore, Polygon’s zkEVM is entering its testnet stage aiming for a 2023 launch.
In addition, Polygon successfully attracts major brands to use its layer 2 platforms. Some of them are Robinhood which wants to make web3 wallets, the Starbucks NFT platform, and cooperation with Meta. to integrate NFTs.
Applications built on Polygon: Aave, OpenSea, Uniswap V3, Curve, Balancer, and Benji Bananas.
Optimism
Optimism (OP) is a 2 Ethereum layer project established in 2019. It utilizes optimistic Rollup technology to reduce transaction costs and speed up the process. As previously explained, Optimistic Rollup can take advantage of Ethereum’s security without having to face its network congestion. Optimism transaction fees are almost 90% cheaper than Ethereum. Optimism has the 3rd largest TVL (Total Value Locked) after Polygon and Arbitrum. This also applies to on-chain data on daily transactions and active wallet addresses.
In its launch, optimism utilizes Airdrop to attract the attention of the Crypto community. One of its ways is to get users to complete many tasks (optimism quest) related to using optimism to get OP.
In Q1 2023, optimism will launch the Bedrock update that would make Optimism an L2 with the cheapest transaction fees. Optimism also mentioned that bedrock became the foundation for the next update, Cannon, a more up-to-date interactive fraud-proof system. If Bedrock is successfully implemented, it will provide a huge advantage for optimism to become the dominant L2 in Ethereum.
Applications built above Optimism: OpenSea, Velodrome, Synthetix, and Aave V3.
Arbitrum
Arbitrum is a Crypto L2 project developed by Offchain Labs and runs since 2021. Like optimism, Arbitrum utilizes optimistic rollup technology that batch transactions and processes them off-chain. This makes transactions on arbitrum much faster and cheaper. At present (January 27, 2023), Additionally, Arbitrum has the second largest TVL in the layer 2 sector which is $1.17 billion.
Arbitrum also has two L2 that run parallel, Arbitrum One, and Nova. One is Arbitrum’s main chain using Optimistic Rollup while Arbitrum Nova is Anytrust Chain. Anytrust Chain has a higher TPS and lower transaction costs but sacrifice decentralization. Arbitrum Nova is designed to meet the needs of developers who need high TPS such as games or trading platforms.
In August 2022, Arbitrum successfully completed its biggest update, Arbitrum Nitro. With Nitro, Arbitrum TPS increases 7-10x, transaction costs are getting cheaper and increasing its compatibility with Ethereum. Nitro also updates the ArbOS, an arbitrum execution machine or AVM (Arbitrum Virtual Machine). The reason Nitro becomes a significant update for arbitrum is Geth integration into AVM. As a result, transactions and contracts in Arbitrum are automatically compatible and synced with Ethereum’s mainnet.
Geth or Go-Ethereum is the implementation of the GO programming language (Golang) into Ethereum. Geth is a popular programming language integrated into EVM.
Applications built on Arbitrum: GMX, OpenSea, Curve, Uniswap V3, and Treasuryao.
ZK Projects
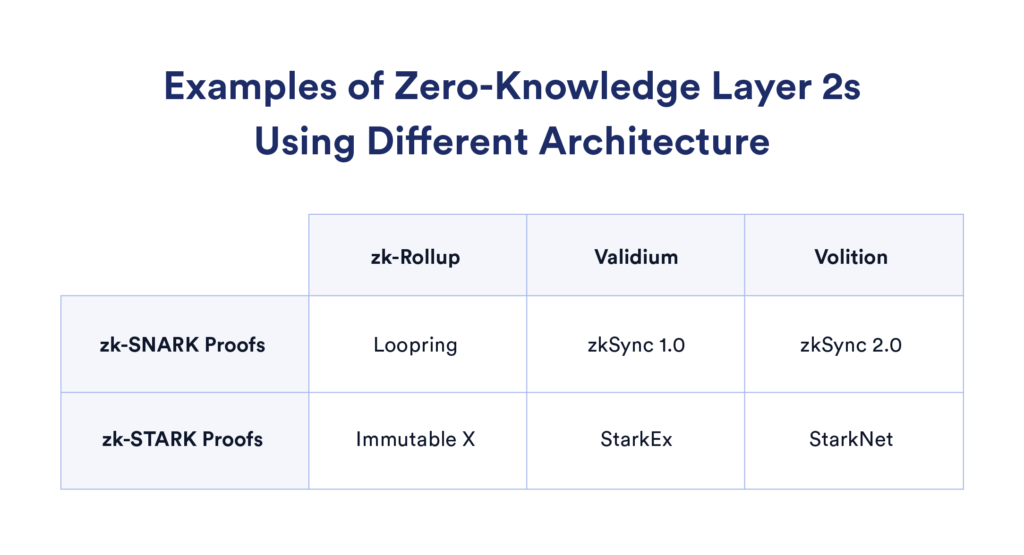
Zero Knowledge technology gets a lot of attention in 2022. Several crypto projects such as dYdX, Loopring, and Immutable X succeeded in applying ZK technology. Loopring and dYdX are decentralized trading platforms that can use high TPS from ZK technology. This year, many ZK projects are focusing on further developing the implementation of ZK, especially in its compatibility with Ethereum. However, the complex nature of ZK is also a barrier to broader implementation in the technology.
As in the picture above, ZK technology also has many variations, with various projects opting for different implementations. Polygon’s ZK project focuses on the use of ZK-STARK while platforms such as Loopring implement ZK-SNARK.
Beyond that, the zkEVM project is also very important because ZK technology is yet to have compatibility with EVM. At present, there are three crypto projects that are developing zkEVM: Polygon, Scroll, and Zksync. ZkEVM implementation can be a significant milestone in encouraging the implementation of ZK in Ethereum.
Potential for Layer 2 in 2023?
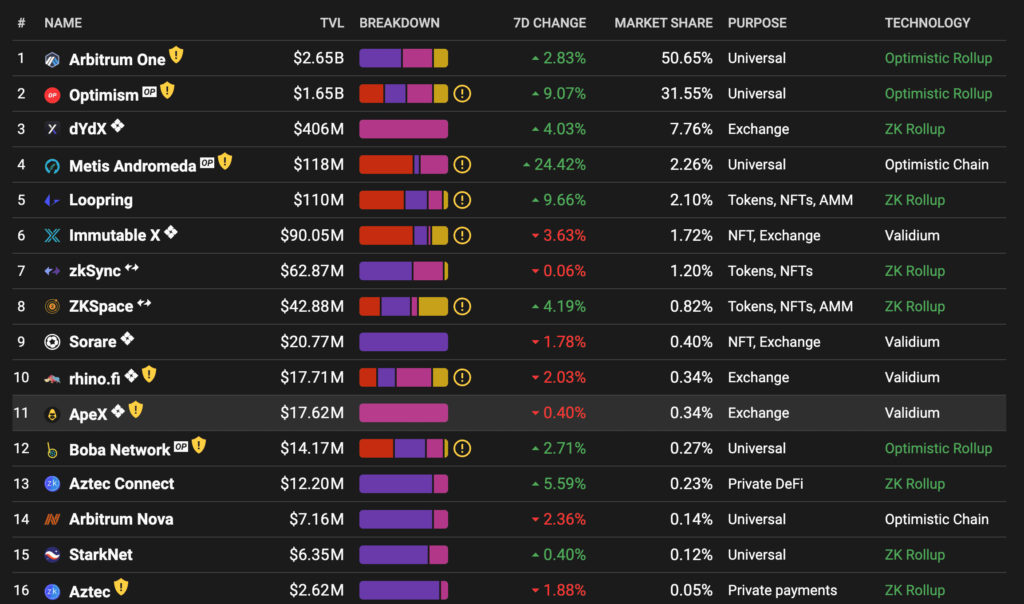
Several crypto research companies such as Messari and Delphi said that the L2 narratives will be big in 2023. This potential comes from on-chain data that shows exponential growth in two L2: Arbitrum and Optimism projects. Both of them continue to get new users even though 2022 is a violent bear market. Furthermore, both of these L2 projects have only been released in the last 2 years. Polygon is also an important player in the L2 sector because it can grab new markets by establishing cooperation with many large brands.
ZK technology also enlivened the L2 sector in 2023. The scaling solution competition between Rollup and ZK will be more fierce with many ZK projects launching this year.
In addition, 2023 will also be an important year for Ethereum. L2 is in a very good position after the Merge. Shanghai, EOF, and Proto-Danksharding upgrades will provide huge benefits for all L2 projects, especially Optimistic Rollup. All of these updates will increase the competitive value of Ethereum by increasing the performance of Ethereum applications and the L2 blockchain on it.
Some L2 assets and applications that you can pay attention to in 2023 are MATIC, OP, IMX, LRC, and Arbitrum Token (which will be launched this year).
Buying Cryptocurrencies in Pintu
You can start investing in cryptocurrencies by buying them in the Pintu app. Here’s how to buy crypto on the Pintu application:
- Create a Pintu account and follow the process of verifying your identity to start trading.
- On the homepage, click the deposit button and top up the Pintu balance using your preferred payment method.
- Go to the market page and look for your favorite crypto assets.
- Click buy and fill in the amount you want.
- Now you have crypto as an asset!
In addition, the Pintu application is compatible with various popular digital wallets such as Metamask to facilitate your transactions. You can download the Pintu cryptocurrency app on Play Store and App Store! Pintu is regulated and supervised by CoFTRA and Kominfo.
You can also learn crypto through the various Door Academy articles which are updated every week! All Pintu Academy articles are for educational purposes, not financial advice.
References
- Layer 2, Ethereum, accessed on 23 January 2023.
- A beginner’s guide on blockchain layer-2 scaling solutions, Coin Telegraph, accessed on 23 January 2023.
- Mason Marcobello, What Are Layer 2s and Why Are They Important?, Coin Desk, accessed on 24 January 2023.
- L2 Brief: Factors That Will Influence zkEVM Adoption, Messari, accessed on 24 January 2023.
- ConsenSys, 2023 CMC Crypto Playbook: The Present and Future of Layer 2 Roll-ups, CoinMarketCap, accessed on 24 January 2023.
- Polygon 2022 Rewind, Polygon Blog, accessed on 25 January 2023.
- Kunal Goel, Optimism: A Glass Half Full, Messari, accessed on 25 January 2023.
- Offchain Labs, Arbitrum Nitro: one small step for L2, one giant leap for Ethereum, Medium, accessed on 26 January 2023.
- Bastian Simpertigue, Arbitrum Nitro – Learn How It Works And Why Is Better, Chain Stack, accessed on 26 January 2023.
- Overview Of Zero-Knowledge Blockchain Projects, Chainlink Blog, accessed on 27 January 2023.
- What Is a Zero-Knowledge Proof (ZKP)?, Chainlink Blog, accessed on 27 January 2023.
Share
Related Article
See Assets in This Article
GAS Price (24 Hours)
Market Capitalization
-
Global Volume (24 Hours)
-
Circulating Supply
-