What is Blockchain Scalability?
The crypto industry still faces a significant issue in blockchain scalability. As long as this issue remains unresolved, mass adoption of blockchain still has a long way to go. Fortunately, the developers always create various innovations to overcome scalability. The result? Slowly, the level of blockchain scalability continues to improve. What exactly is the cause? What are the solutions to overcome it? Check out the full story
Article Summary
- ⚡ Blockchain scalability refers to the system’s ability to handle many transactions quickly and efficiently. Scalability is measured by latency, throughput, and operational costs.
- 🚫 Unfortunately, blockchain is still outmatched in terms of scalability compared to centralized networks like Visa and PayPal. This is one reason that is hindering the mass adoption of blockchain.
- ♻️ Scalability is part of the blockchain trilemma, balancing decentralization, security, and scalability. Increasing scalability often comes at the cost of decreasing decentralization or security.
- Technologies such as Segregated Witness, Sharding, Sidechains, Rollups, and Zero-Knowledge exist as solutions to improve blockchain scalability.
What is Blockchain Scalability?
Projected to replace existing technologies, blockchain is still faced with one serious major problem: scalability. What exactly is blockchain scalability? Simply put, it refers to the speed at which transactions are processed. There are three metrics used in measuring the scalability of a blockchain:
- Latency or the time it takes to send a transaction across nodes and collect their responses to reach a consensus. Lower latency will result in a network with better scalability.
- Throughput or the number of transactions processed in one second (TPS). The higher the throughput, the better the scalability will be.
- Cost. The resources (computation power, bandwidth, etc.) required to run a blockchain determine its scalability. More resources would mean higher network incentives, especially for more network participants. If the incentives are not commensurate, it will discourage network users.
As we know, blockchain scalability is still inferior to centralized networks such as Visa and PayPal. The blockchain scalability problem ultimately results in long transaction processing and expensive fees. This is the reason why the mass adoption rate of blockchain technology is hampered.
Blockchain Scalability Problems
When discussing blockchain scalability, it cannot be separated from the blockchain trilemma. It is a problem faced by the development team when building a blockchain. The reason is that when creating a blockchain, there are three main aspects to consider: decentralization, security, and scalability.
Ideally, a blockchain can maximize all three aspects. However, with the current technology, developers are faced with the choice to “sacrifice” one aspect to maximize the other two. This condition of being trapped in a dilemma (in this case, a trilemma) is referred to as the blockchain trilemma. Ethereum Co-Founder Vitalik Buterin is the person who popularized the concept of blockchain trilemma.
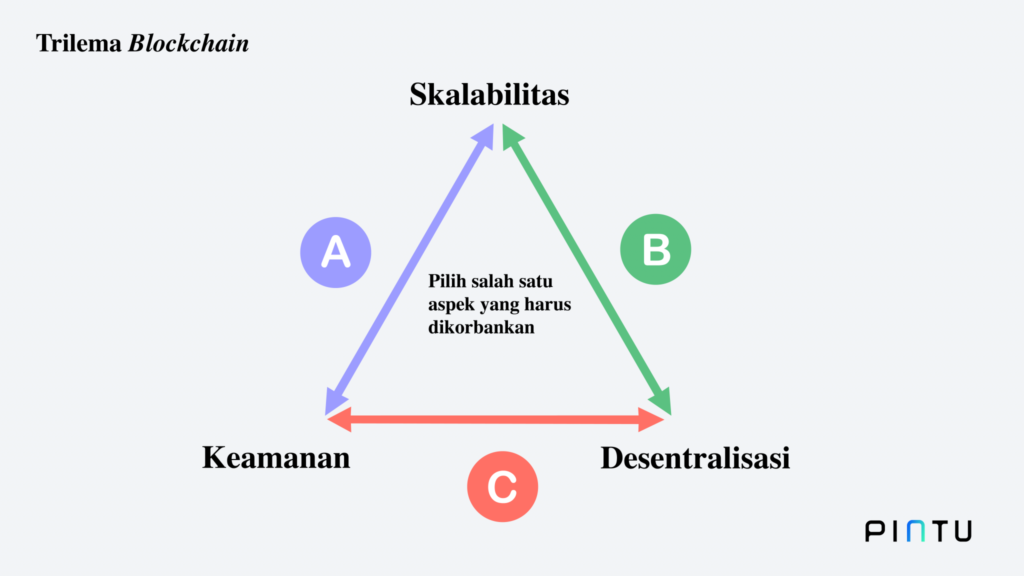
With blockchain’s prioritized security and decentralized aspect, the scalability has to be sacrificed. This has led to the low scalability of blockchain. Pintu Academy has prepared a special article that discusses the blockchain trilemma phenomenon in detail here.
Why is Blockchain Scalability Important?
Scalability in blockchain is crucial because it affects the network’s ability to process transactions. With good scalability, blockchains can maintain processing speed and network efficiency even as the number of transactions and users increases.
Most blockchains today have no problem processing a small number of transactions or a small number of users. They can maintain a good level of scalability while being secure and decentralized.
However, when the number of users and transactions increases, transaction processing becomes slower and more expensive. On the Ethereum network, for example, when the network is congested, gas fees can be as high as US$100. This hurts the user experience. If it continues, users will eventually be reluctant to use blockchain. Thus impacting the adoption rate and growth of blockchain itself.
Blockchain Scalability Solutions
Developers have created various technological breakthroughs as solutions for blockchain scalability. Starting from utilizing layer 1 technology to layer 2. The following solutions have successfully made blockchain scalability better.
Layer 1 Solution
1. Segregated Witness
Segregated Witness or SEGWIT is an update to the Bitcoin network that reduces the weight of transactions within a blockchain block. It works by separating the signature data from the transactions in each block. This process frees up space and increases the block’s capacity to hold more transactions.
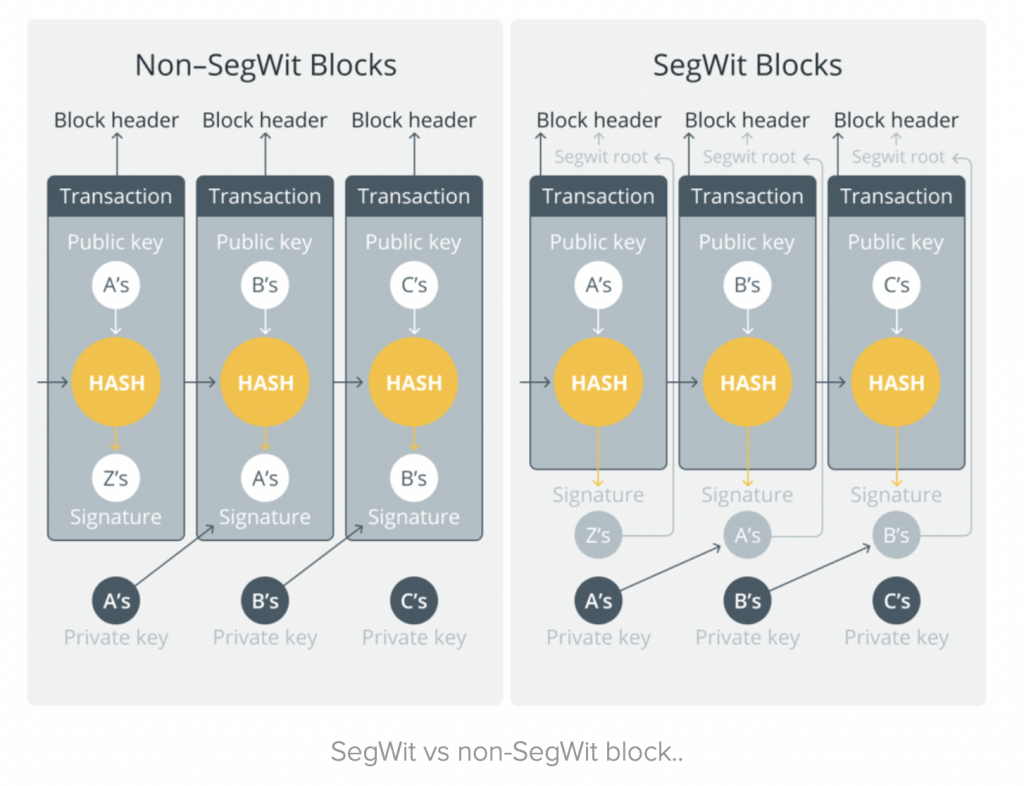
As the number of transactions that can fit in a block becomes larger, the number of transaction queues in the mempool also becomes smaller. The segwit update makes Bitcoin transaction confirmation faster.
2. Sharding
Sharding is a blockchain architecture that allows each node to store only a tiny portion of the blockchain’s data. Through sharding, the data storage process is divided into smaller shards, which different parties can store. Simultaneously, this process divides the computational and data storage load across multiple nodes, reducing the overall network load
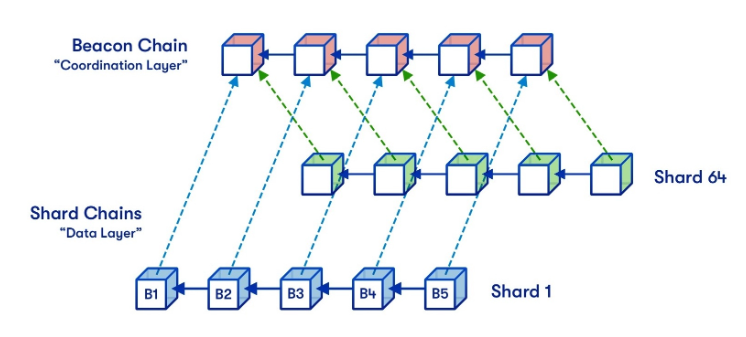
As a result, sharding can increase network speed and scalability without compromising security and decentralization. One blockchain that has implemented sharding to increase scalability is Near Protocol. Through the Merge, Ethereum is now also utilizing sharding technology.
In the following article, you can learn more about how sharding works in the Ethereum blockchain.
Layer 2 Solutions
1. Sidechains
Sidechain’s scalability solution is by creating a separate chain that is connected to the main chain through a bridge with its consensus mechanism. This allows users to make transactions on the sidechain without affecting the performance of the main blockchain. As a result, the burden on the main blockchain to validate transactions becomes lighter.
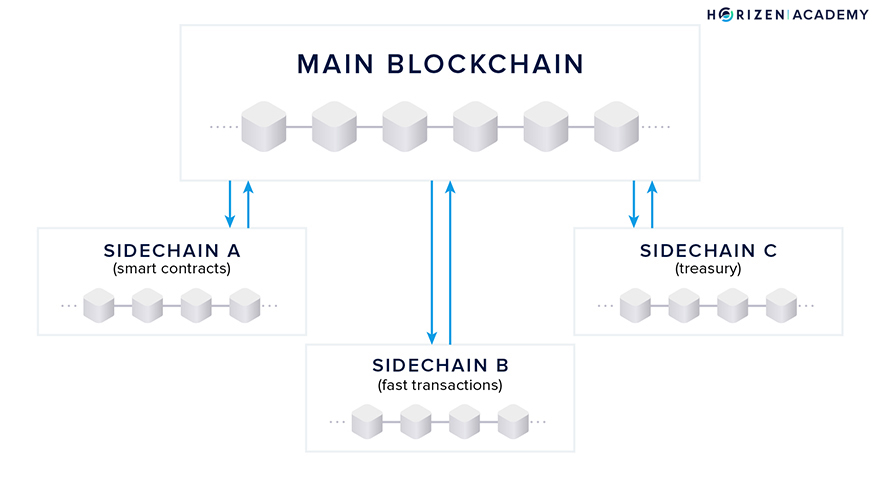
In addition to having their consensus mechanism, sidechains can also be designed for specific use cases. Polygon is one example of a network successfully implementing sidechains as a scalability solution. However, the security in a sidechain is separate and does not utilize the main network security.
2. Rollups
Rollup is one of Ethereum’s scalability solutions that ‘rolls up’ a batch of transactions into one at layer 2 and sends them back to the L1 (Ethereum) network. In this way, rollup can reduce transaction fees, and speed up transactions, while reducing the load on the Ethereum network.
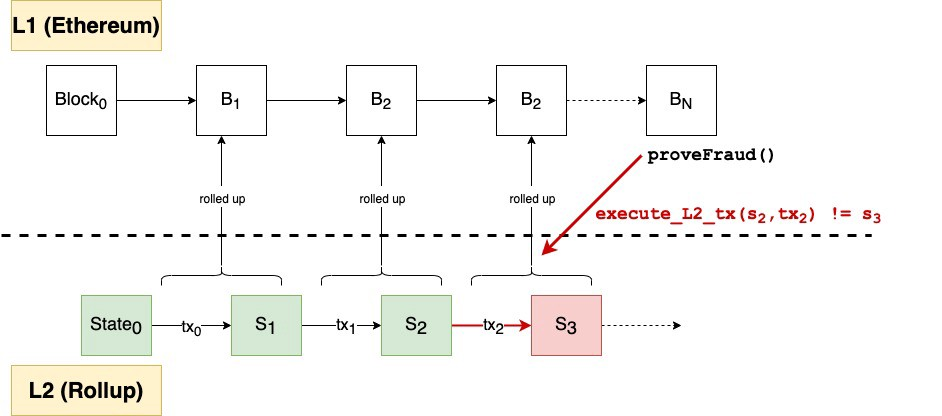
Through rollup, around 2,000 transactions can be rolled up into a single batch. As a result, the transaction size, which is usually 112 bytes on Ethereum, becomes only 12 bytes after rollup. Once the transactions are combined, the validator will send it back to Ethereum. This removes the heavy computation and data storage on the L2. Therefore, rollup-type L2 is an option for many projects because it offers lower transaction fees while utilizing Ethereum’s security.
Read an article about What is Layer 2 at Pintu Academy.
3. Zero Knowledge
Zero-Knowledge (ZK) is an advanced cryptographic method of passing information without revealing its entire information as proof. The use of ZK can help blockchains increase scalability while maintaining security.
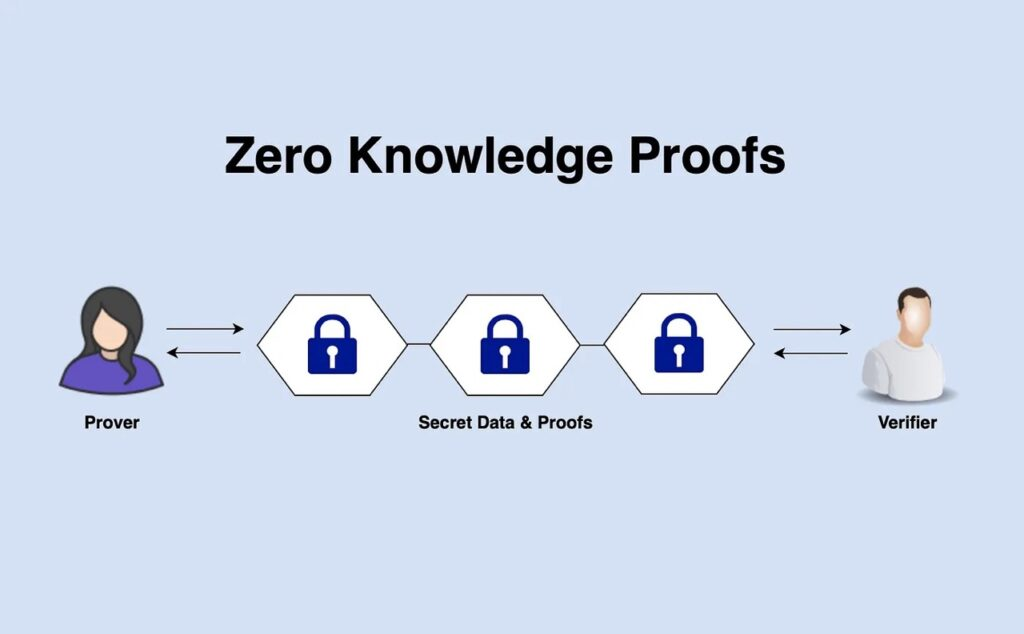
The ZK method allows transactions to be verified without revealing sensitive data in them. It also cuts down on transaction verification time. This is because the network only needs to check the ZK proof without having to process all the transactions it carries. Currently, Ethereum is a testing ground for the development of various ZK technologies.
Currently, zero-knowledge and ZKP technologies are still challenging to implement due to their high cost and complexity. Polygon is one of the leading teams on ZK-based system. In addition, some other crypto projects that implement ZK technology are StarkNet, StarkEx, and zkSync.
Conclusion
Blockchain has the potential to change the world with all its technology. However, this will only be realized if the scalability problem has been resolved. Users will be willing to use blockchain if the transaction process is fast and affordable.
Mass adoption will only be achieved when the development team can create a blockchain with high scalability. Fortunately, development teams are constantly innovating to develop solutions for blockchain scalability. With all the potential that exists, the opportunity to continue to increase blockchain scalability is still wide open.
Buy Crypto Assets on Pintu
Looking to invest in crypto assets? No worries, you can safely and conveniently purchase a wide range of cryptocurrencies such as BTC, ETH, SOL, and others safely and easily on Pintu. Pintu diligently evaluates all its crypto assets, highlighting the significance of being cautious.
Pintu is also compatible with popular wallets such as Metamask to facilitate your transactions. Download Pintu app on Play Store and App Store! Your security is guaranteed because Pintu is regulated and supervised by Bappebti and Kominfo.
Aside from buying and trading crypto assets, you can expand your knowledge about cryptocurrencies through various Pintu Academy articles. Updated weekly, all Pintu Academy articles are made for knowledge and educational purposes, not as financial advice
References
- Shardeum, What is Blockchain Scalability? A Deep Dive Guide, accessed on 1 November 2023.
- Chainlink, Blockchain Scalability: Execution, Storage, and Consensus, accessed on 1 November 2023.
- Blockchain Council, “Optimistic Rollups vs. Zero-Knowledge (ZK) Rollups: How Do They Work?”, accessed on 1 November 2023.
Share


