What is Blockchain Trilemma?
The term blockchain trilemma refers to an issue encountered by today’s decentralized platforms, which emphasize that each blockchain can only focus on 2 of its 3 main advantages: decentralization, security, and scalability. This means that the development team is faced with the choice of sacrificing one of these three aspects. So, is there a way to resolve this issue? Check the following article for a detailed explanation.
Article Summary
- ⚠️ The blockchain trilemma is a problem when a developer has to sacrifice one aspect of decentralization, security, and scalability.
- 🚧 Scalability is one of the aspects that the developer is currently focusing on for the broader adoption of blockchain.
- 🔗 The presence of technologies such as layer-1 and layer-2 is the most effective way to optimize the scalability of a blockchain.
What is Blockchain Trilemma?
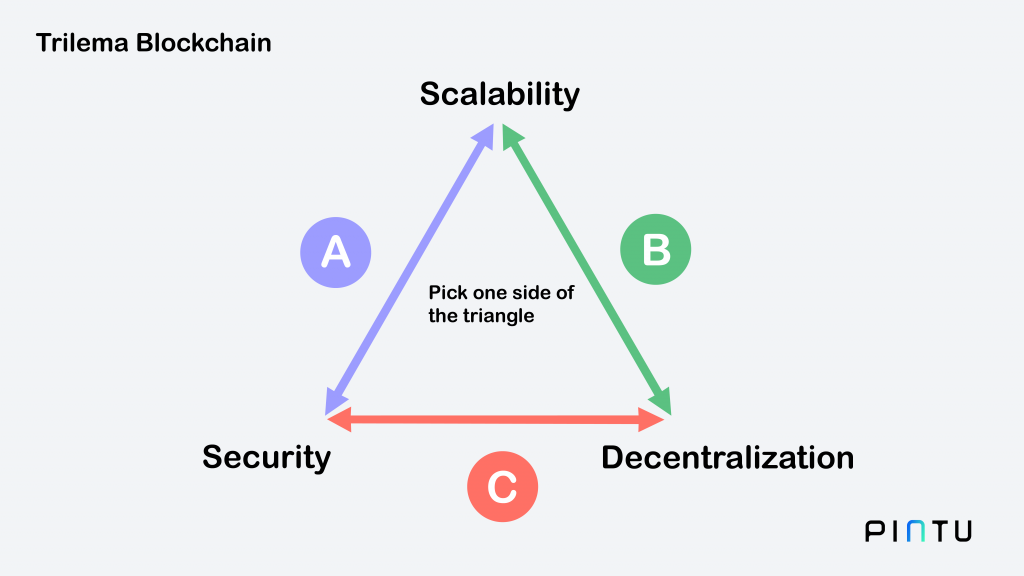
The three most important aspects that blockchain developers consider while building a blockchain are decentralization, security, and scalability. In reality, though, the developer must choose whether to “sacrifice” one component in favor of the other two. The condition of being stuck in a dilemma (in this case, the trilemma) is referred to as the blockchain trilemma. Ethereum Co-Founder Vitalik Buterin is the one who popularized the blockchain trilemma concept.
Blockchain Trilemma Aspects
Decentralization
Decentralization is a notion that makes the blockchain system independent from a single central governing entity. This is one of the main distinctions between blockchain and traditional networks, which are still centralized.
This decentralized system is also important because it encourages ownership without control, meaning everyone can use the platform. Every decision is determined by a consensus, and each transaction is approved by several nodes as opposed to just one.
Security
The security of a blockchain can differ from one to another. In a public blockchain, validators or users use the internet to validate transactions and reach a consensus. This leaves the blockchain in a vulnerable position to attacks by hackers. Thus, the security aspect is vital for every blockchain.
Scalability
A blockchain must have good scalability so it can quickly process many user transactions. But, the transaction fees must remain affordable. Scalability is important because it is related to mass adoption. Blockchain with a slow transaction processing speed will not be used by many people.
💡 These three aspects also apply to traditional networks. Visa, for example, is sacrificing decentralization to optimize its scalability and security aspects. This means every transaction in the network is controlled by Visa. But, in return, they can process a higher number of transactions, as compared to a decentralized network while maintaining network security.
How Did Trilemma Blockchain Happen?
In reality, the current blockchain has yet to be able to optimize all of the three aspects mentioned. Like it or not, with current technology, developers must sacrifice one This is what ultimately led to the blockchain trilemma.
If you want the highest security and scalability, the decentralization component will be weaker as the control is held only by a few parties. If optimizing decentralization and security are the main priorities, then it will take longer to verify transactions due to the spread of control, hence lower scalability. Lastly, if decentralization and scalability are prioritized, the security aspect will be weaker. When there are fewer participants, the blockchain is more vulnerable to attacks.
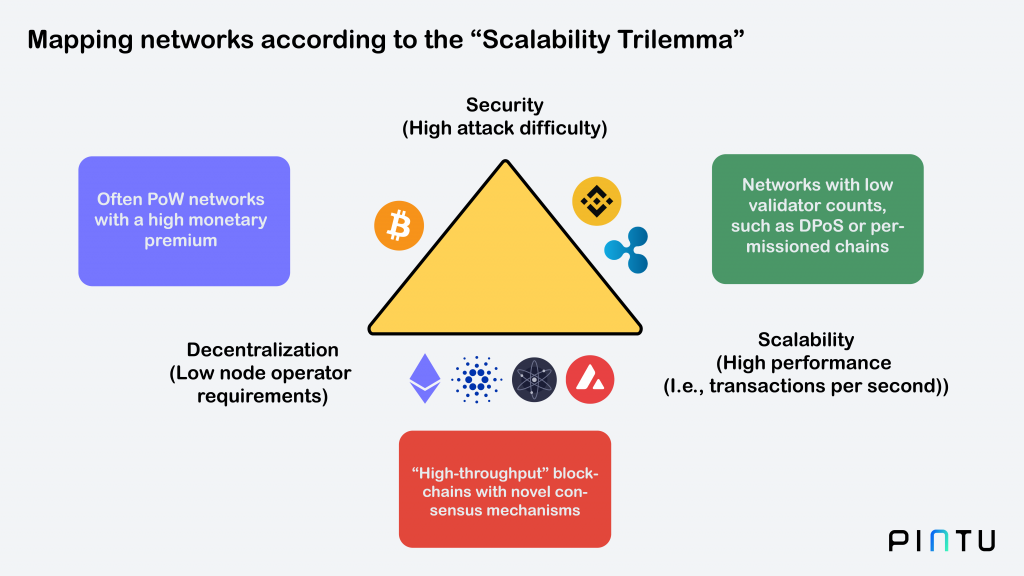
An example of the blockchain trilemma can be seen in the Bitcoin blockchain. As we know, the Bitcoin blockchain prioritizes its decentralization aspect where no central party controls it. In addition, the Bitcoin blockchain also has a level of security that is impossible to hack. One way to ensure security, Bitcoin implements a combination of cryptography and a Proof-of-Work (PoW) consensus mechanism. With the PoW mechanism, the more participants in a network, the more secure the network will be.
You can learn more about Bitcoin PoW mechanism in the following article
However, Bitcoin must sacrifice the scalability aspect to maximize the two aspects above. With a decentralized network, every transaction must be processed by all participants through the PoW mechanism. Of course, this process cannot take place immediately. As a result, Bitcoin can only process seven transactions per second. Try to compare it with a centralized network like Visa, which can process 63,000 transactions per second.
How to Solve Blockchain Trilemma
There hasn’t been a clear solution to the blockchain trilemma as of yet. However, here are a few methods that aim to solve the blockchain trilemma:
Layer-1
In a decentralized ecosystem, Layer-1 refers to blockchain protocols such as Bitcoin, Litecoin, and Ethereum. Currently, several methods are developed to improve blockchain scalability directly.
- Consensus Protocol Improvements
Despite the slow transaction speed, the PoW mechanism is one of the most secure protocols. Blockchains such as Bitcoin and Litecoin use PoW consensus. Ethereum also previously used PoW mechanism, but it recently switched to Proof-of-Stake (PoS) to increase its scalability.
Instead of relying on miners to verify transactions through mining, PoS requires validators to lock up their crypto assets to secure the network and verify transactions. With this mechanism, the transaction process can be much faster. Besides PoS, there are other consensus protocols, for example, Solana’s Proof-of-History (PoH).
If you are interested in finding out how Solana’s PoH works, don’t forget to read the following article.
- Sharding
Sharding is a blockchain architecture that allows each node (computer/server) to process verification to store a small part of the platform’s data. Through sharding, the data storage process is divided into smaller shards, which can be stored in various parties. Simultaneously, this process divides the computing and data storage load across multiple nodes. Thus, reducing the overall burden.
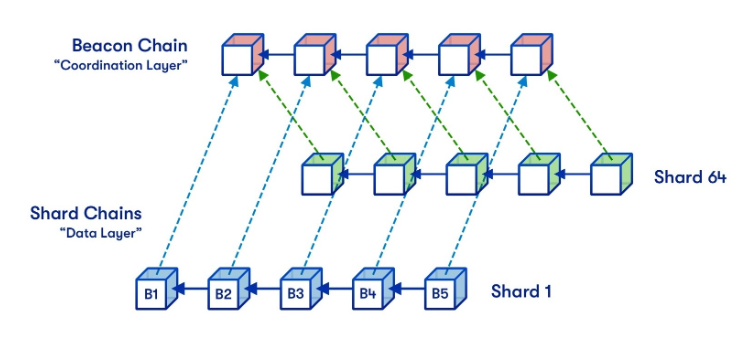
As a result, sharding can increase network speed and scalability without compromising security and decentralization. One blockchain that implements sharding to increase scalability is Near Protocol. Through the Merge, Ethereum is now also utilizing sharding technology.
In the following article, you can find an explanation of how Sharding works on the Ethereum blockchain.
Layer 2
Layer-2 refers to a network or technology that operates on top of an existing blockchain protocol. It aims to improve the scalability and efficiency of the underlying blockchain (Layer-1). Layer-2 protocols have been continuously developing lately and can be one way to overcome scalability problems, especially for PoW consensus.
- Rollups
Rollups are the most commonly used layer-2 solution for increasing scalability. Rollups work by combining several layer-2 transactions and then sending them as one transaction to the main blockchain. This system uses validity proofs to ensure the integrity of a transaction.
- Zero-Knowledge Proofs
Zero-Knowledge (ZK) is a subset of cryptography that allows someone to prove they know or have a piece of data without disclosing the underlying information. The use of ZK technology can help the blockchain to overcome the scalability aspect while maintaining the security aspect. This is because ZK technology can verify transactions faster. After all, it only requires ZK-proof data instead of processing the entire data. As all data does not need to be processed, this also protects the privacy of the data owners. Polygon is one blockchain keen to develop and implement the ZK proofs system in its network. Apart from that, several other crypto projects trying to implement ZK technology are StarkNet, StarkEx, and zkSync.
Click on the following article to find out more about Polygon technology.
- Sidechains
Sidechains are a combination of state channels and nested blockchains. Sidechains will connect layer-1 with the main blockchain via a bridge that has its consensus mechanism. Thus, the burden on the main blockchain to validate transactions becomes lighter. Typically, sidechains are used for a large group of transactions. An example is a game with the largest blockchain, Axie Infinity, which connects its Ronin sidechain to Ethereum.
In the following article, you can get to know more about the ecosystem and technology presented by Axie Infinity.
The following table provides a brief explanation of the differences between Layer-1 and Layer-2.
| Criteria | Layer-1 | Layer-2 |
| Definition | Layer-1 refers to a base network like Bitcoin and Ethereum. Scaling solutions for Layer-1 means modifications in the base protocol of the blockchain network to achieve better scalability. | Layer-2 scaling solutions involve the use of off-chain services or networks to improve scalability. |
| Working | Changes in the base protocol, such as larger block sizes or new consensus mechanisms, can empower scalability. | Sharing the transaction ordering and processing workload with off-chain solutions improves scalability. |
| Types | – Consensus protocol improvement – Modifications in block sizes – Sharding | – Rollups – Zero-Knowledge Proofs – State Channels – Sidechains |
Can the Blockchain Trilemma Be Solved?
So far, there has yet to be a definite solution to solving the blockchain trilemma. Current technology does not allow developers to optimize aspects of decentralization, security, and scalability simultaneously. In the future, the blockchain trilemma problem can be solved when technology becomes more sophisticated so that the speed of blockchain transactions can be maximized without sacrificing decentralization and security.
However, for now, solutions such as Layer-1 and Layer-2, as well as various other efforts, are the best way to optimize blockchain capabilities. The developers are still trying and optimistic that they can solve the blockchain trilemma. Therefore, we should also put this trust and be confident that the blockchain trilemma can be solved in the future.
Start Investing at Pintu
You can start investing on DApps tokens such as, UNI, COMP, AAVE, and others through Pintu App. Through Pintu, you can invest in various crypto assets such as BTC, BNB, ETH, and others safely and easily.
Pintu is also compatible with popular wallets such as Metamask to facilitate your transactions. Download Pintu app on Play Store and App Store! Your security is guaranteed because Pintu is regulated and supervised by Bappebti and Kominfo.
In addition to executing transactions, in the Pintu Apps, you can also learn more about crypto through various Pintu Academy articles which are updated every week! All Pintu Academy articles are made for knowledge and educational purposes, not as a financial advice.
Reference
CertiK, The Blockchain Trilemma: Decentralized, Scalable, and Secure? CertiK Blog, accessed on 27 November 2022.
Alexandria, Blockchain Trilemma, Coinmarketcap, accessed on 26 November 2022.
Bybit Learn, The Blockchain Trilemma: Can It Ever Be Solved? Bybit, accessed on 26 November 2022.
Mohammad Musharraf, What is the Blockchain Trilemma? Ledger Academy, accessed on 26 November 2022.
Rahul Nambiarmpurath, What Are Layer 1 and Layer 2 Blockchain Networks? The Defiant, accessed on 27 November 2022.
Cryptopedia, Layer-1 and Layer-2 Blockchain Scaling Solutions, Gemini, accessed on 27 November 2022.
Chainlink, Overview of Zero-Knowledge Blockchain Projects, Chainlink Blog, accessed on 27 November 2022.
Share