What is Perpetual Futures Trading?
Perpetual futures allow you to trade crypto with experience similar to spot trading, but with enhanced flexibility and potential for higher profits. First, you can use leverage to amplify your trading power, opening positions up to 25x-50x larger than your initial capital. Additionally, unlike traditional spot trading where you can only make profit by buying low and selling high, perpetual futures allow you to profit even in falling markets through shorting—selling an asset now and buying it back later at a lower price.
Perpetual futures contract have no expiration date, giving you the freedom to hold positions as long as you want just like holding spot asset, making them a powerful tool for navigating both rising and falling market trends. While the opportunities are significant, understanding the risks, including pricing mechanisms like mark price valuation and funding rates, is crucial for successful trading.
In this article, we’ll break down how perpetual futures work and what you need to know before trading.
Article Summary
- Perpetual futures are a type of derivative product that tracks the price of an underlying crypto asset. They allow you to take both long and short positions, enabling you to profit in both bullish and bearish markets. Key mechanisms such as mark price valuation and funding rate settlements provide stability by anchoring the futures prices to the spot price.
- Leverage is another key feature of perpetual futures, allowing you to open larger positions with relatively small amounts of capital. While leverage amplifies potential profits, it also increases risk, including the chance of liquidation if the market moves against you.
- Margin management is a critical component of perpetual futures trading. Margin acts as collateral to cover potential losses. You must maintain an initial margin to open positions and a maintenance margin to avoid liquidation. If the account balance falls below the maintenance margin, the position may be liquidated, potentially leading to additional costs covered by the exchange’s insurance fund. Understanding and monitoring margin requirements and liquidation thresholds are essential for effective risk management.
How Does Perpetual Futures Work?
To understand how perpetual futures work, there are several key concepts you need to know. These are the features that distinguish this type of trading from regular spot trading.
Long & Short Positions
Perpetual futures provide you with the ability to profit from market movements in any direction. You can take long positions to benefit from price increases or short positions to profit from price declines.
- Long Position: A long position is taken when you anticipate that the price of the underlying cryptocurrency will rise. By opening a long position, you buy the asset at the current price, and if the price increases, you can sell or close the position to realize a profit. This strategy is ideal for bullish market conditions.
- Short Position: On the other hand, shorting allows you to profit when the market is going down. In a short position, you sell at the current price, expecting the contract’s value to drop. Once the price decreases, you buy back the contract at the lower price to close off your position, pocketing the difference as profit. This mechanism makes perpetual futures particularly appealing during bearish market trends.
The ability to take both long and short positions is a core feature of perpetual futures, enabling you to navigate various market conditions and hedge against potential losses in your broader portfolios. However, both strategies require a solid understanding of market dynamics and effective risk management to avoid significant losses, particularly when leverage is involved.
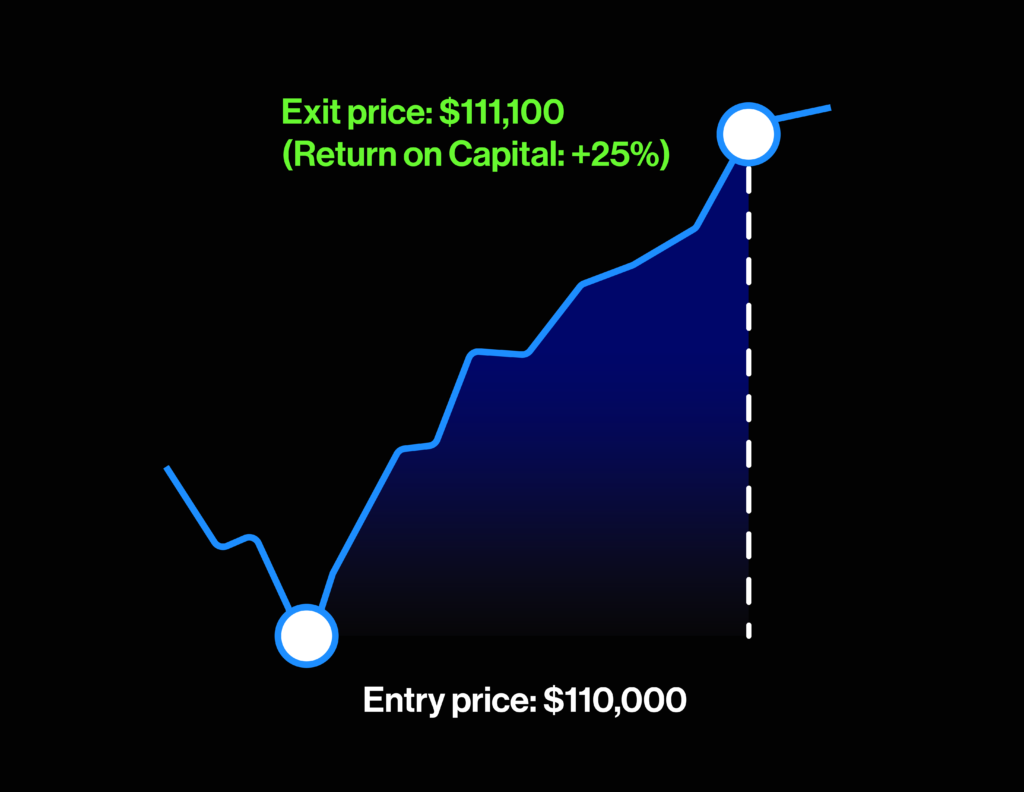
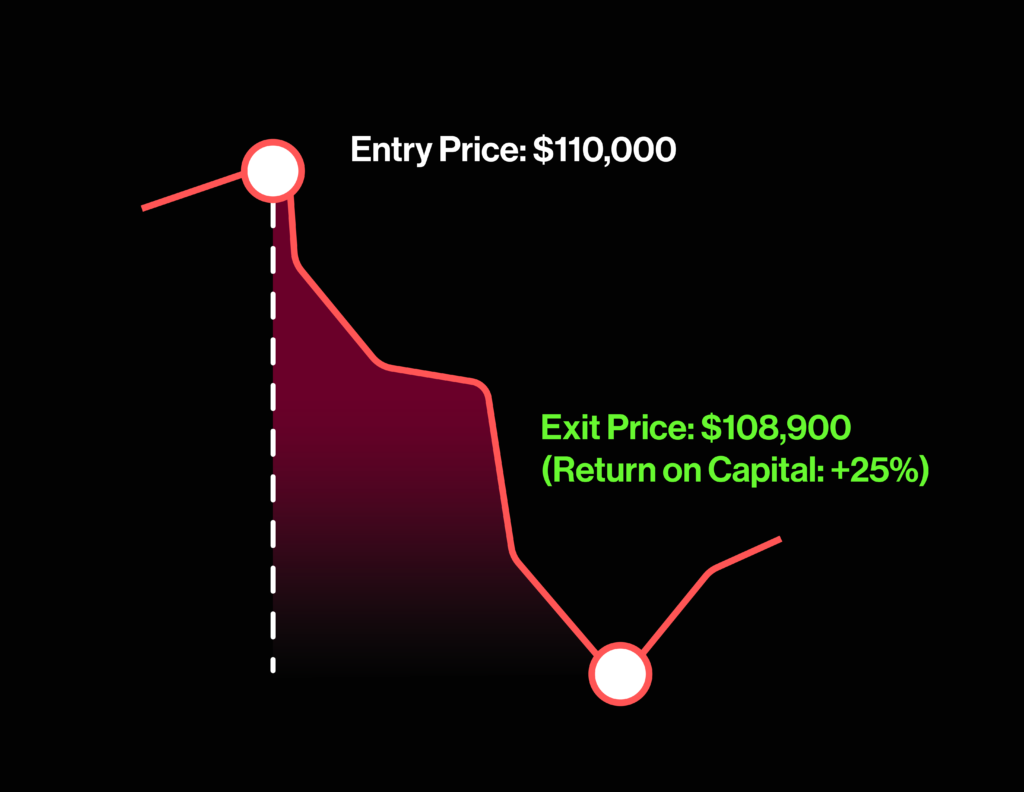
Below are illustrations showing how to profit whether the price is rising or falling.
Mark Price
Perpetual futures use the “Mark Price” to calculate unrealized profit and loss (PnL) and determine liquidation thresholds. Mark Price is derived from the weighted average of spot prices across leading exchanges, ensuring price stability and reducing susceptibility to market manipulation.
Pro Tip: Monitor Mark Price closely, especially during periods of high volatility. Significant deviations between Mark Price and Trade Price can indicate speculative activity and heightened risk.
Trading Profit & Loss (PnL)
In Perpetual futures, Profit & Loss (PnL) comes in two forms—unrealized and realized—and each plays a critical role in managing your trading performance and risk. Understanding these will help you make informed decisions and better manage your positions in both volatile and stable market conditions.
- Unrealized PnL – Unrealized PnL is an estimation of your position’s profit or loss prior to actually closing the position. This metric is used in a process known as marking to market, which ensures that your gains and losses are accounted for even before you exit the position. Marking to market is particularly important because perpetual futures are traded on leverage, and this mechanism prevents you from losing more than you have. Monitoring unrealized PnL can help you assess your current position and make adjustments if necessary.
- Realized PnL – Realized PnL is the final profit or loss amount that is settled when you close out your position. Unlike unrealized PnL, which is based on the Mark Price, realized PnL is calculated using the actual trading price at which you exit the position.
Funding Rate
The primary purpose of the funding rate is to prevent significant price discrepancies between perpetual futures and the underlying spot market. When the perpetual futures price deviates substantially from the spot price, the funding rate comes into play to help bring the prices back into alignment by incentivizing traders to take positions that counteract the current market trend, thereby reducing the price gap.
The funding rate can be either positive or negative.
- A positive funding rate occurs when the perpetual trades above the spot price. In this case, long position holders pay a fee for short positions; by imposing additional funding charges on the long position holders, it encourages people to factor in the additional cost and potentially long less or even go short if the funding rate is very high.
- A negative funding rate occurs when the perpetual trades below the spot price. Here, short position holders pay a fee to long position holders; opposite to a positive funding rate, a negative funding rate may encourage people to short less, and hence removing some of the selling pressure to allow the futures prices to return increase back to the level of the index price.
Funding rates can help you execute perpetual trades more optimally. Learn how here.
Leverage
While you need to have 100% of your funds in advance to trade spot, perpetual futures allows you to use leverage, which means that you only need to put up a fraction of the order value instead. For example, if you want to buy $100 worth of BTC in spot, you will need to have $100 in purchase power. However, buy $100 worth of BTC through a 25x perpetual futures, you will only need to produce the initial margin, which is just 4% of the $100 (i.e. $100 / 25), or simply $4. In this example, trading perpetual futures has reduced the amount of capital needed by 96%!
The advantage of using leverage is that it amplifies your potential profits (i.e. you only need $4 to gain exposure to $100 worth of BTC). But as you will quickly see, leverage can be a double edged sword – while it boosts your potential profits significantly if you predicted the market correctly, if the market goes against you, you have a high risk of being liquidated and losing all your funds in a cross margin account. Below grid demonstrates how leverage can lower your capital requirement and dramatically boost your return on capital.
| Leverage | Position | Capital Required | PnL if Price Increases 1% | Return on Capital |
| 50x | 100 USDT | 2 USDT | 1 USDT | 50% |
| 25x | 100 USDT | 4 USDT | 1 USDT | 25% |
| 10x | 100 USDT | 10 USDT | 1 USDT | 10% |
| 5x | 100 USDT | 20 USDT | 1 USDT | 5% |
| Spot Trading | 100 USDT | 100 USDT | 1 USDT | 1% |

Margin
Margin is essentially the collateral that you put up against the exchange to cover for the potential losses that your position may suffer. Remember from the previous example, you only provided $4 of margin to open a $100 BTC position, the $4 is used to cover for any losses that the position may suffer, and you can see that if the $100 BTC position loses more than $4, you will actually have no money left to cover for any additional losses – so this is the fundamental reason why Exchanges like CFX will setup thresholds to make sure that this does not happen and that your position will be closed before losing more than $4.
There are 3 main margin concepts to pay attention to when trading perpetual futures:
- Initial Margin – this is the amount of funds you must have in your account in order to open a new position. This is usually defined as a % of the position value you are trying to open. The % may vary depending on the leverage you are using. In our example of 25x, the initial margin is 1/25 or 4% of the value you are trying to trade.
- Maintenance Margin – this is the amount of funds that you must maintain to avoid having your position closed. Usually this amount is set to be 1/4 of your initial margin. So with 25x leverage, the maintenance margin will be 1%. In other words, to open a $100 position, you need to start with $4 of Initial Margin, and need to make sure you don’t let your margin account drop to $1 or the Maintenance Margin threshold, otherwise your position will be liquidated and you will lose all your funds.
💡 Important to note: initial margin is only locked for open orders. Once an open order is filled and converts into an open position, only the maintenance margin is locked. So if you start with a $4 margin balance, when you open a $100 new order, all $4 of the margin balance will be locked. However, once the order is filled and you now have a $100 position, only $1 will be locked. The remaining $3 of margin balance will actually be freed up to deploy again, but by re-using the $3 available margin, you will be be increasing your leverage to beyond 25x, which is not advisable.
3. Margin Usage Ratio – margin usage ratio, which is a key value that Pintu provides its users is a way for you to keep track of the overall risk level of your position. As you open more positions and use more leverage, this ratio will increase. If this ratio reaches 100%, you will be liquidated. This is a more intuitive way to understand the overall health of your account and the risk of liquidation.
Liquidation
If you are unable to keep your margin account balance above the maintenance margin threshold (i.e. because your position is losing or you have over leveraged your account and the maintenance margin threshold is very high), then your account will be liquidated. When liquidation happens, CFX (as the Exchange) will take over your losing position and all the remaining available margin.
- Liquidation Price – The liquidation price is the estimated price point at which your unrealized PnL losses will bring your margin balance will below the maintenance margin threshold and trigger a liquidation. If you have multiple positions, this number may fluctuate depending on the unrealized PnL from other positions, so it is always important to monitor your liquidation price together with the maintenance margin usage %.
- Insurance Fund – The exact process of liquidation is extremely intricate and complex, but at high level, what the liquidation engine aims to achieve is to help exit the liquidated positions in the market without incurring additional losses and also minimizing any adverse market impact. In cases where the liquidation was completed without incurring additional losses, any excess margin will be contributed to the CFX exchange’s insurance fund, which will be used to cover for any excess losses beyond what the exchange has taken over (this is the scenario if you opened a $100 BTC position with only $4 of margin, and the position ended up losing $10 – the extra $6 of losses will have to be covered by the insurance fund).
Reminder: Track your liquidation price regularly to avoid unexpected liquidations.
Conclusion
Perpetual trading offers opportunities for traders interested in speculating on the future price of crypto assets without expiration dates. With leverage, perpetual trading also presents the potential for higher profits than spot trading.
However, perpetual trading also carries higher risks compared to spot trading. Traders must be more careful in managing leverage usage, margin requirements, and risk management strategies. If miscalculated, a trader’s futures account can be liquidated, resulting in the loss of all invested capital. Therefore, in-depth research, understanding how the system works, and having a clear risk management plan before engaging in perpetual trading are essential.
How to Start Trading on Pintu
You can buy crypto assets like BTC, SOL, and many others directly through Pintu Pro Web. This platform allows you to trade both Futures and Spot conveniently in one place.
Here’s how to Futures on Pintu Pro Web:
- Visit https://pintu.co.id/
- Click the Futures button at the top center.
- Click Trade Futures on Desktop.
- Register or log in to Pintu Pro Web.
- Start trading BTC and other cryptocurrencies.
FAQ
1. What is the main difference between perpetual trading and traditional futures?
Perpetual trading has no expiration date, while traditional futures have a fixed maturity date.
2. How does perpetual trading keep contract prices aligned with spot prices?
It uses mechanisms like mark price and funding rate to maintain price stability close to the spot market.
3. What is the main benefit of using leverage in perpetual trading?
Leverage allows traders to open larger positions with smaller capital, increasing potential gains.
4. What risks should be understood before starting perpetual trading?
Key risks include rapid liquidation, high volatility, and potential losses exceeding your initial margin without proper risk management.
All articles provided by Pintu Academy are for educational purposes only and do not constitute financial advice.
Reference:
- Adam Hayes, Perpetual Futures: What They Are and How They Work, Investopedia, Accessed 19 September 2024.
- Ary Palaguna, Memahami Perpetual Trading Kripto dan Cara Kerjanya, Coinvestasi, Accessed 19 September 2024.
- Alpha Point, Perpetual Futures: How They Work & Pros and Cons, Accessed 19 September 2024.
Share